Targeted disruption of Aldh1a1 (Raldh1) provides evidence for a complex mechanism of retinoic acid synthesis in the developing retina
- PMID: 12808103
- PMCID: PMC164835
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.13.4637-4648.2003
Targeted disruption of Aldh1a1 (Raldh1) provides evidence for a complex mechanism of retinoic acid synthesis in the developing retina
Abstract
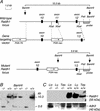
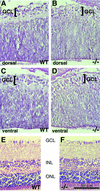
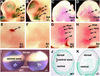
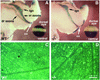
Genetic studies have shown that retinoic acid (RA) signaling is required for mouse retina development, controlled in part by an RA-generating aldehyde dehydrogenase encoded by Aldh1a2 (Raldh2) expressed transiently in the optic vesicles. We examined the function of a related gene, Aldh1a1 (Raldh1), expressed throughout development in the dorsal retina. Raldh1(-/-) mice are viable and exhibit apparently normal retinal morphology despite a complete absence of Raldh1 protein in the dorsal neural retina. RA signaling in the optic cup, detected by using a RARE-lacZ transgene, is not significantly altered in Raldh1(-/-) embryos at embryonic day 10.5, possibly due to normal expression of Aldh1a3 (Raldh3) in dorsal retinal pigment epithelium and ventral neural retina. However, at E16.5 when Raldh3 is expressed ventrally but not dorsally, Raldh1(-/-) embryos lack RARE-lacZ expression in the dorsal retina and its retinocollicular axonal projections, whereas normal RARE-lacZ expression is detected in the ventral retina and its axonal projections. Retrograde labeling of adult Raldh1(-/-) retinal ganglion cells indicated that dorsal retinal axons project to the superior colliculus, and electroretinography revealed no defect of adult visual function, suggesting that dorsal RA signaling is unnecessary for retinal ganglion cell axonal outgrowth. We observed that RA synthesis in liver of Raldh1(-/-) mice was greatly reduced, thus showing that Raldh1 indeed participates in RA synthesis in vivo. Our findings suggest that RA signaling may be necessary only during early stages of retina development and that if RA synthesis is needed in dorsal retina, it is catalyzed by multiple enzymes, including Raldh1.
Figures
References
-
- Ang, H. L., and G. Duester. 1999. Retinoic acid biosynthetic enzyme ALDH1 localizes in a subset of retinoid-dependent tissues during Xenopus development. Dev. Dyn. 215:264-272. - PubMed
-
- Ang, H. L., and G. Duester. 1999. Stimulation of premature retinoic acid synthesis in Xenopus embryos following premature expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH1. Eur. J. Biochem. 260:227-234. - PubMed
-
- Chapman, D. L., N. Garvey, S. Hancock, M. Alexiou, S. I. Agulnik, J. J. Gibson-Brown, J. Cebra-Thomas, R. J. Bollag, L. M. Silver, and V. E. Papaioannou. 1996. Expression of the T-box family genes, Tbx1-Tbx5, during early mouse development. Dev. Dyn. 206:379-390. - PubMed
-
- Collins, M. D., C. Eckhoff, I. Chahoud, G. Bochert, and H. Nau. 1992. 4-Methylpyrazole partially ameliorated the teratogenicity of retinol and reduced the metabolic formation of all-trans-retinoic acid in the mouse. Arch. Toxicol. 66:652-659. - PubMed
-
- Deltour, L., R. J. Haselbeck, H. L. Ang, and G. Duester. 1997. Localization of class I and class IV alcohol dehydrogenases in mouse testis and epididymis: potential retinol dehydrogenases for endogenous retinoic acid synthesis. Biol. Reprod. 56:102-109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
