Nova regulates GABA(A) receptor gamma2 alternative splicing via a distal downstream UCAU-rich intronic splicing enhancer
- PMID: 12808107
- PMCID: PMC164843
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.13.4687-4700.2003
Nova regulates GABA(A) receptor gamma2 alternative splicing via a distal downstream UCAU-rich intronic splicing enhancer
Abstract
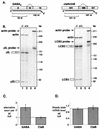
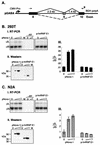
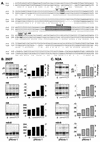
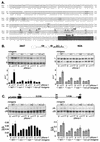
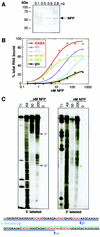
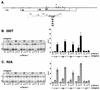
Nova is a neuron-specific RNA binding protein targeted in patients with the autoimmune disorder paraneoplastic opsoclonus-myoclonus ataxia, which is characterized by failure of inhibition of brainstem and spinal motor systems. Here, we have biochemically confirmed the observation that splicing regulation of the inhibitory GABA(A) receptor gamma2 (GABA(A)Rgamma2) subunit pre-mRNA exon E9 is disrupted in mice lacking Nova-1. To elucidate the mechanism by which Nova-1 regulates GABA(A)Rgamma2 alternative splicing, we systematically screened minigenes derived from the GABA(A)Rgamma2 and human beta-globin genes for their ability to support Nova-dependent splicing in transient transfection assays. These studies demonstrate that Nova-1 acts directly on GABA(A)Rgamma2 pre-mRNA to regulate E9 splicing and identify an intronic region that is necessary and sufficient for Nova-dependent enhancement of exon inclusion, which we term the NISE (Nova-dependent intronic splicing enhancer) element. The NISE element (located 80 nucleotides upstream of the splice acceptor site of the downstream exon E10) is composed of repeats of the sequence YCAY, consistent with previous studies of the mechanism by which Nova binds RNA. Mutation of these repeats abolishes binding of Nova-1 to the RNA in vitro and Nova-dependent splicing regulation in vivo. These data provide a molecular basis for understanding Nova regulation of GABA(A)Rgamma2 alternative splicing and suggest that general dysregulation of Nova's splicing enhancer function may underlie the neurologic defects seen in Nova's absence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nova autoregulation reveals dual functions in neuronal splicing.EMBO J. 2005 Apr 20;24(8):1608-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600630. Epub 2005 Mar 31. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15933722 Free PMC article.
-
An RNA map predicting Nova-dependent splicing regulation.Nature. 2006 Nov 30;444(7119):580-6. doi: 10.1038/nature05304. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Nature. 2006. PMID: 17065982
-
Nova-1 regulates neuron-specific alternative splicing and is essential for neuronal viability.Neuron. 2000 Feb;25(2):359-71. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80900-9. Neuron. 2000. PMID: 10719891
-
The neuronal splicing factor Nova controls alternative splicing in N-type and P-type CaV2 calcium channels.Channels (Austin). 2010 Nov-Dec;4(6):483-9. doi: 10.4161/chan.4.6.12868. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Channels (Austin). 2010. PMID: 21150296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional and mechanistic insights from genome-wide studies of splicing regulation in the brain.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;623:148-60. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77374-2_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18380345 Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved RNA switch for acetylcholine receptor clustering at neuromuscular junctions in chordates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 6:2024.07.05.602308. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.05.602308. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39005407 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Electroacupuncture at PC6 (Neiguan) Attenuates Angina Pectoris in Rats with Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Regulating the Alternative Splicing of the Major Inhibitory Neurotransmitter Receptor GABRG2.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022 Oct;15(5):1176-1191. doi: 10.1007/s12265-022-10245-w. Epub 2022 Apr 4. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35377129
-
Nova1 is a master regulator of alternative splicing in pancreatic beta cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct;42(18):11818-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku861. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25249621 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-RNA and protein-protein recognition by dual KH1/2 domains of the neuronal splicing factor Nova-1.Structure. 2011 Jul 13;19(7):930-44. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2011.05.002. Structure. 2011. PMID: 21742260 Free PMC article.
-
NOVA1 promotes NSCLC proliferation and invasion by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.BMC Cancer. 2022 Oct 25;22(1):1091. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10164-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36284263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amara, S. G., V. Jonas, M. G. Rosenfeld, E. S. Ong, and R. M. Evans. 1982. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature 298:240-244. - PubMed
-
- Berget, S. M. 1995. Exon recognition in vertebrate splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 270:2411-2414. - PubMed
-
- Bubunenko, M., T. L. Kress, U. D. Vempati, K. L. Mowry, and M. L. King. 2002. A consensus RNA signal that directs germ layer determinants to the vegetal cortex of Xenopus oocytes. Dev. Biol. 248:82-92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
