X-linked stapes gusher: CT findings in one patient
- PMID: 12812938
- PMCID: PMC8149040
X-linked stapes gusher: CT findings in one patient
Abstract
A 31-year-old male patient presented with progressive mixed hearing loss since birth. A stapedectomy was attempted and was unsuccessful because of perilymph gushing. CT of the temporal bones showed bulbous dilatation of the fundi of the internal auditory canals and absence of the bone plates separating them from the base of the cochleas. This unusual abnormality was found after the attempted stapedectomy and explains the clinical findings. The findings in male patients are fairly typical X-linked congenital deafness.
Figures
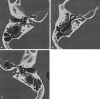
Similar articles
-
CT and MRI findings in X-linked progressive deafness.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2008 Sep;14(3):117-9. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18814129
-
Computed tomographic findings of X-linked deafness: a spectrum from child to mother, from young to old, from boy to girl, from mixed to sudden hearing loss.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014 Jan-Feb;38(1):20-4. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0b013e3182a0d05f. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014. PMID: 24424552
-
X-linked deafness, stapes gushers and a distinctive defect of the inner ear.Neuroradiology. 1991;33(4):326-30. doi: 10.1007/BF00587816. Neuroradiology. 1991. PMID: 1922747
-
Congenital anomalies of the inner ear.Radiol Clin North Am. 1974 Dec;12(3):473-82. Radiol Clin North Am. 1974. PMID: 4612590 Review. No abstract available.
-
Congenital malformations of the ear and cochlear implantation in children: review and temporal bone report of common cavity.J Laryngol Otol Suppl. 2000;25:1-14. doi: 10.1258/0022215001904842. J Laryngol Otol Suppl. 2000. PMID: 10824232 Review.
Cited by
-
Audiovestibular Quantification in Rare Third Window Disorders in Children.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 16;11:954. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00954. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33041966 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric sensorineural hearing loss, part 2: syndromic and acquired causes.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012 Mar;33(3):399-406. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2499. Epub 2011 May 19. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012. PMID: 21596810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spectrum of Third Window Abnormalities: Semicircular Canal Dehiscence and Beyond.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Jan;38(1):2-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4922. Epub 2016 Aug 25. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 27561833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel and De Novo Mutations Extend Association of POU3F4 with Distinct Clinical and Radiological Phenotype of Hearing Loss.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 12;11(12):e0166618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166618. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27941975 Free PMC article.
-
Inner-Ear Disorders Presenting with Air-Bone Gaps: A Review.J Int Adv Otol. 2020 Apr;16(1):111-116. doi: 10.5152/iao.2020.7764. J Int Adv Otol. 2020. PMID: 32401207 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nance WE, Setleff R, McLedd A, et al. X-linked deafness with congenital fixation of the stapedial footplate and perilymphatic gusher. Birth Defects 1971;7:64–69 - PubMed
-
- Wallis C, Ballo R, Wallis G. X-linked mixed deafness with stapes fixation in a Mauritian kindred: linkage to Xq probe pDP34. Genomics 1998;3:299–301 - PubMed
-
- Phleps PD, Reardon W, Pembrey M, et al. X-linked deafness, stapes gushers, and a distinctive defect of the inner ear. Neuroradiology 1991;33:326–330 - PubMed
-
- Talbot JM, Wilson DF. Computed tomographic diagnosis of X-linked congenital mixed deafness, fixation of the stapedial footplate, and perilymphatic gusher. Am J Otol 1994;15:177–182 - PubMed
-
- Tang A, Parnes LS. X-linked progressive mixed hearing loss: computed tomography findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1994;103:655–657 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
