Sensitivity-encoded diffusion tensor MR imaging of the cervical cord
- PMID: 12812966
- PMCID: PMC8149014
Sensitivity-encoded diffusion tensor MR imaging of the cervical cord
Abstract
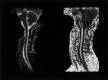
The aim of this study was to apply sensitivity-encoding (SENSE) echo-planar imaging (EPI) to diffusion tensor MR imaging of the cervical cord, an anatomic region where MR imaging is particularly challenging. This technique was implemented with a SENSE reduction factor of 2 and used for imaging a water phantom and five healthy volunteers. Off-resonance artifacts were notably reduced compared with those of full-FOV EPI sequences. This approach to diffusion tensor MR imaging of the cervical cord is promising for future, more extensive clinical applications.
Figures
References
-
- Pruessman KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 1999;42:952–962 - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D. Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin-echo. J Magn Reson B 1994;103:247–254 - PubMed
-
- Sodickson DK, Manning W. Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn Reson Med 1997;38:591–603 - PubMed
-
- Bammer R, Keeling SL, Augustin M, et al. Improved diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar imaging (EPI) in stroke using sensitivity encoding (SENSE). Magn Reson Med 2001;46:548–554 - PubMed
-
- Bammer R, Auer M, Keeling SL, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging using single-shot SENSE-EPI. Magn Reson Med 2002;48:128–136 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
