Archaeal homolog of bacterial type IV prepilin signal peptidases with broad substrate specificity
- PMID: 12813086
- PMCID: PMC161584
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.13.3918-3925.2003
Archaeal homolog of bacterial type IV prepilin signal peptidases with broad substrate specificity
Abstract
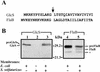
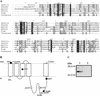
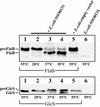
A large number of secretory proteins in the thermoacidophile Sulfolobus solfataricus are synthesized as a precursor with an unusual leader peptide that resembles bacterial type IV prepilin signal sequences. This set of proteins includes the flagellin subunit but also various solute binding proteins. Here we describe the identification of the S. solfataricus homolog of bacterial type IV prepilin peptidases, termed PibD. PibD is an integral membrane protein that is phylogenetically related to the bacterial enzymes. When heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli, PibD is capable of processing both the flagellin and glucose-binding protein (GlcS) precursors. Site-directed mutagenesis of the GlcS signal peptide shows that the substrate specificity of PibD is consistent with the variations found in proteins with type IV prepilin-like signal sequences of S. solfataricus. We conclude that PibD is responsible for the processing of these secretory proteins in S. solfataricus.
Figures

References
-
- Albers, S. V., and A. J. M. Driessen. 2002. Signal peptides of secreted proteins of the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus: a genomic survey. Arch. Microbiol. 177:209-216. - PubMed
-
- Albers, S. V., W. N. Konings, and A. J. M. Driessen. 1999. A unique short signal sequence in membrane-anchored proteins of Archaea. Mol. Microbiol. 31:1595-1596. - PubMed
-
- Bardy, S. L., and K. F. Jarrell. 2002. FlaK of the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis possesses preflagellin peptidase activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 208:53-59. - PubMed
-
- Bayley, D. P., and K. F. Jarrell. 1998. Further evidence to suggest that archaeal flagella are related to bacterial type IV pili. J. Mol. Evol. 46:370-373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

