Characterization and functional complementation of a nonlethal deletion in the chromosome of a beta-glycosidase mutant of Sulfolobus solfataricus
- PMID: 12813089
- PMCID: PMC161586
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.13.3948-3957.2003
Characterization and functional complementation of a nonlethal deletion in the chromosome of a beta-glycosidase mutant of Sulfolobus solfataricus
Abstract
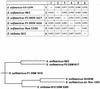
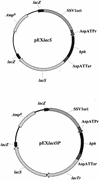
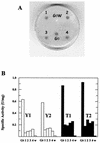
LacS(-) mutants of Sulfolobus solfataricus defective in beta-glycosidase activity were isolated in order to explore genomic instability and exploit novel strategies for transformation and complementation. One of the mutants showed a stable phenotype with no reversion; analysis of its chromosome revealed the total absence of the beta-glycosidase gene (lacS). Fine mapping performed in comparison to the genomic sequence of S. solfataricus P2 indicated an extended deletion of approximately 13 kb. The sequence analysis also revealed that this chromosomal rearrangement was a nonconservative transposition event driven by the mobile insertion sequence element ISC1058. In order to complement the LacS(-) phenotype, an expression vector was constructed by inserting the lacS coding sequence with its 5' and 3' flanking regions into the pEXSs plasmid. Since no transformant could be recovered by selection on lactose as the sole nutrient, another plasmid construct containing a larger genomic fragment was tested for complementation; this region also comprised the lacTr (lactose transporter) gene encoding a putative membrane protein homologous to the major facilitator superfamily. Cells transformed with both genes were able to form colonies on lactose plates and to be stained with the beta-glycosidase chromogenic substrate X-Gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl-beta-D-galactopyranoside).
Figures




References
-
- Aagaard, C., I. Leviev, R. N. Aravalli, P. Forterre, D. Prieur, and G. A. Garrett. 1996. General vectors for archaeal hyperthermophiles: strategies based on a mobile intron and a plasmid. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 18:93-104. - PubMed
-
- Ammendola, S., L. Politi, and R. Scandurra. 1998. Cloning and sequencing of ISC1041 from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus MT-4, a new member of the IS30 family of insertion elements. FEBS Lett. 428:217-223. - PubMed
-
- Aravalli, R. N., and R. A. Garrett. 1997. Shuttle vectors for hyperthermophilic Archaea. Extremophiles 1:183-191. - PubMed
-
- Arnold, H. P., Q. She, H. Phan, K. Stedman, D. Prangishvili, I. Holz, J. K. Kristjansson, R. Garrett, and W. Zillig. 1999. The genetic element pSSVx of the extremely thermophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus is a hybrid between a plasmid and a virus. Mol. Microbiol. 34:217-226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

