Polymorphic hydroxylation of perhexiline in vitro
- PMID: 12814462
- PMCID: PMC1884253
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01805.x
Polymorphic hydroxylation of perhexiline in vitro
Abstract
Aims: The aims of this study were to examine the in vitro enzyme kinetics and CYP isoform selectivity of perhexiline monohydroxylation using human liver microsomes.
Methods: Conversion of rac-perhexiline to monohydroxyperhexiline by human liver microsomes was assessed using a high-performance liquid chromatography assay with precolumn derivatization to measure the formation rate of the product. Isoform selective inhibitors were used to define the CYP isoform profile of perhexiline monohydroxylation.
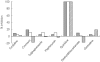
Results: The rate of perhexiline monohydroxylation with microsomes from 20 livers varied 50-fold. The activity in 18 phenotypic perhexiline extensive metabolizer (PEM) livers varied about five-fold. The apparent Km was 3.3 +/- 1.5 micro m, the Vmax was 9.1 +/- 3.1 pmol min-1 mg-1 microsomal protein and the in vitro intrinsic clearance (Vmax/Km) was 2.9 +/- 0.5 micro l min-1 mg-1 microsomal protein in the extensive metabolizer livers. The corresponding values in the poor metabolizer livers were: apparent Km 124 +/- 141 micro m; Vmax 1.4 +/- 0.6 pmol min-1 mg-1 microsomal protein; and intrinsic clearance 0.026 micro l min-1 mg-1 microsomal protein. Quinidine almost completely inhibited perhexiline monohydroxylation activity, but inhibitors selective for other CYP isoforms had little effect.
Conclusions: Perhexiline monohydroxylation is almost exclusively catalysed by CYP2D6 with activities being about 100-fold lower in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers than in extensive metabolizers. The in vitro data predict the in vivo saturable metabolism and pharmacogenetics of perhexiline.
Figures
 , H12; □, H25;
, H12; □, H25;  , H27.
, H27.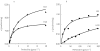
Similar articles
-
CYP2B6, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 catalyze the primary oxidative metabolism of perhexiline enantiomers by human liver microsomes.Drug Metab Dispos. 2007 Jan;35(1):128-38. doi: 10.1124/dmd.106.012252. Epub 2006 Oct 18. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007. PMID: 17050648
-
Effect of CYP2D6 metabolizer status on the disposition of the (+) and (-) enantiomers of perhexiline in patients with myocardial ischaemia.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2007 May;17(5):305-12. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e32800ffba0. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17429312
-
Correlation of CYP2D6 genotype with perhexiline phenotypic metabolizer status.Pharmacogenetics. 2003 Oct;13(10):627-32. doi: 10.1097/00008571-200310000-00006. Pharmacogenetics. 2003. PMID: 14515061
-
Steady-state pharmacokinetics of the enantiomers of perhexiline in CYP2D6 poor and extensive metabolizers administered Rac-perhexiline.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;65(3):347-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.03015.x. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17875193 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of CYP2D6 content and metoprolol oxidation between microsomes isolated from human livers and small intestines.Pharm Res. 1999 Aug;16(8):1199-205. doi: 10.1023/a:1018989211864. Pharm Res. 1999. PMID: 10468020
Cited by
-
Drug Metabolism of Hepatocyte-like Organoids and Their Applicability in In Vitro Toxicity Testing.Molecules. 2023 Jan 7;28(2):621. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020621. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677681 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: Part I.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48(11):689-723. doi: 10.2165/11318030-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009. PMID: 19817501 Review.
-
Clinical inhibition of CYP2D6-catalysed metabolism by the antianginal agent perhexiline.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Apr;57(4):456-63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.02033.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15025744 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lipid degradation promotes prostate cancer cell survival.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 13;8(24):38264-38275. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16123. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415728 Free PMC article.
-
Phenoconversion of Cytochrome P450 Metabolism: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 7;9(9):2890. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092890. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32906709 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beaugrand M, Poupon R, Levy VG, Callard P, Lageron A, Lecomte D, et al. Hepatic lesions due to perhexiline maleate. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1978;2:579–588. - PubMed
-
- Pessayre D, Bichara M, Degott C, Potet F, Benhamou JP, Feldmann G. Perhexiline maleate-induced cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1979;76:170–177. - PubMed
-
- Hay DR, Gwynne JF. Cirrhosis of the liver following therapy with perhexiline maleate. NZ Med J. 1983;96:202–204. - PubMed
-
- Paliard P, Vitrey D, Fournier G, Belhadjali J, Patricot L, Berger F. Perhexiline maleate-induced hepatitis. Digestion. 1978;17:419–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

