Reversal of age-related learning deficits and brain oxidative stress in mice with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics
- PMID: 12815103
- PMCID: PMC166262
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1332809100
Reversal of age-related learning deficits and brain oxidative stress in mice with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics
Abstract
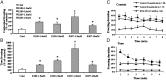
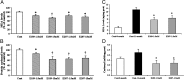
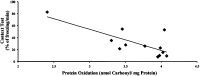
Oxidative stress has been implicated in cognitive impairment in both old experimental animals and aged humans. This implication has led to the notion that antioxidant defense mechanisms in the brain are not sufficient to prevent age-related increase in oxidative damage and that dietary intake of a variety of antioxidants might be beneficial for preserving brain function. Here we report a dramatic loss of learning and memory function from 8 to 11 months of age in mice, associated with marked increases in several markers of brain oxidative stress. Chronic systemic administration of two synthetic catalytic scavengers of reactive oxygen species, Eukarion experimental compounds EUK-189 and EUK-207, from 8 to 11 months almost completely reversed cognitive deficits and increase in oxidative stress taking place during this time period in brain. In particular, increase in protein oxidation was completely prevented, whereas increase in lipid peroxidation was decreased by approximately 50%. In addition, we observed a significant negative correlation between contextual fear learning and levels of protein oxidation in brain. These results further support the role of reactive oxygen species in age-related learning impairment and suggest potential clinical applications for synthetic catalytic scavengers of reactive oxygen species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of cognitive deficits and brain oxidative stress with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics in aged mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2010 Mar;31(3):425-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.05.009. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Neurobiol Aging. 2010. PMID: 18571288 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic EUK-207 in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: protection against and interruption of progression of amyloid and tau pathology and cognitive decline.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30(1):183-208. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111298. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22406441
-
Redox modulation of the liver with chronic antioxidant enzyme mimetic treatment prevents age-related oxidative damage associated with environmental stress.FASEB J. 2004 Oct;18(13):1547-9. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1629fje. Epub 2004 Aug 19. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15319374
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Antioxidants in the Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 28;21(19):7152. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197152. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32998277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant health effects of aged garlic extract.J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3s):1010S-5S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.3.1010S. J Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11238807 Review.
Cited by
-
Attenuation of oxidative damage-associated cognitive decline by Withania somnifera in rat model of streptozotocin-induced cognitive impairment.Protoplasma. 2013 Oct;250(5):1067-78. doi: 10.1007/s00709-013-0482-2. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Protoplasma. 2013. PMID: 23340606
-
Pursuing the Elixir of Life: In Vivo Antioxidative Effects of Manganosalen Complexes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Aug 10;9(8):727. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080727. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32785017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of radiation-induced brain toxicity and implications for future clinical trials.J Neurooncol. 2008 May;87(3):279-86. doi: 10.1007/s11060-008-9520-x. Epub 2008 Jan 22. J Neurooncol. 2008. PMID: 18209952 Review.
-
HIV-1 Vpr disrupts mitochondria axonal transport and accelerates neuronal aging.Neuropharmacology. 2017 May 1;117:364-375. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.02.008. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28212984 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in rat brain induced by carbofuran exposure.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008 Nov;28(7):961-9. doi: 10.1007/s10571-008-9270-5. Epub 2008 Mar 14. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18340526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grady, C. L. & Craik, F. I. (2000) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10 224-231. - PubMed
-
- Dean, R. L., III, Scozzafava, J., Goas, J. A., Regan, B., Beer, B. & Bartus, R. T. (1981) Exp. Aging Res. 7 427-451. - PubMed
-
- Gallagher, M. & Nicolle, M. M. (1993) Behav. Brain Res. 57 155-162. - PubMed
-
- Ingram, D. K., Spangler, E. L., Iijima, S., Ikari, H., Kuo, H., Greig, N. H. & London, E. D. (1994) Life Sci. 55 2037-2049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

