Various types of Dirofilaria immitis polyproteins selectively induce a Th2-Type immune response
- PMID: 12819063
- PMCID: PMC162011
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.7.3802-3811.2003
Various types of Dirofilaria immitis polyproteins selectively induce a Th2-Type immune response
Abstract
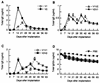
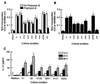
Dirofilaria immitis polyproteins (DiAgs) are found as 15-kDa monomeric and 30-kDa dimeric forms in excretory-secretory products of the adult worm. We evaluated the ability of various types of recombinant DiAg (rDiAg; V1 and V2 as monomers and V1V2, V2V1, V1V1, and V2V2 as dimers) to influence Th1/Th2 immune responses. V1-, V1Vx- and V2-, V2Vx-driven nonspecific immunoglobulin E (IgE) production peaked at 21 and 14 days after administration, respectively. Dimer-induced IgE response was an interesting biphasic pattern with the second peaks on days 35 (V2Vx) or 42 (V1Vx). Absolute amounts of nonspecific IgE production induced with monomers were larger than those observed with dimers at the first peak. The magnitude of cell expansion and interleukin-10 (IL-10) production in mesenteric lymph node (MLN) B-cell induced with rDiAgs was linked to the levels of the first IgE peak in vivo and IgE produced by rDiAg plus IL-4-stimulated B cells in vitro. All rDiAgs failed to augment IgG2c production. V2 and V2Vx elicited IL-4 production by MLN cells more rapidly than V1 and V1Vx. The inhibitory effect of rDiAg on gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) production was stronger in monomers than in dimers. Neutralization of IL-10 restored IFN-gamma production, whereas the expression of IL-4 and IgE was partly prevented by depletion of IL-10. These results indicate that monomer rather than dimer is an efficient form of DiAg and suggest that the difference of IgE-inducing capacity among these DiAgs is closely associated with the pattern of both B-cell activation and IL-4 production.
Figures
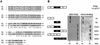

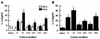

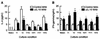

References
-
- Akao, N., K. Kondo, and K. Fujita. 1991. Immunoblot analysis of Dirofilaria immitis recognized by infected humans. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 85:455-460. - PubMed
-
- Bacharier, L. B., H. Jabara, and R. S. Geha. 1998. Molecular mechanisms of immunogloblin E regulation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 115:257-269. - PubMed
-
- Cuellar, C., M. J. Perteguer, and M. Rodero. 2001. Presence of IL-4-like molecules in larval exceretory-secretory and crude extracts from Anisakis simplex. Scand. J. Immunol. 53:483-488. - PubMed
-
- Culpepper, J., R. B. Grieve, L. Friedman, M. Mika-Grieve, G. R. Frank, and B. Dale. 1992. Molecular characterization of a Dirofilaria immitis cDNA encoding a highly immunoreactive antigen. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 54:51-62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

