Recombinant soluble CD14 reduces severity of intramammary infection by Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12819092
- PMCID: PMC161972
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.7.4034-4039.2003
Recombinant soluble CD14 reduces severity of intramammary infection by Escherichia coli
Abstract
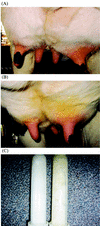
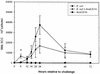
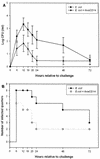
The interaction among gram-negative bacteria, the innate immune system, and soluble CD14 (sCD14) has not been well documented. The effect of recombinant bovine sCD14 (rbosCD14) on milk somatic cell count (SCC), bacterial clearance, and cytokine production was investigated by using a bovine intramammary Escherichia coli infection model. We first determined whether rbosCD14 would increase the SCC during a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. Three quarters of each of six healthy lactating cows were injected with either 0.3 microg of LPS, 0.3 microg of LPS plus 100 micro g of rbosCD14, or saline. In comparison with quarters injected with LPS alone, the SCC was twofold higher (P < 0.05) in quarters injected with LPS plus rbosCD14 after the challenge. We therefore hypothesized that when E. coli bacteria invade the mammary gland, sCD14 in milk would interact with LPS and rapidly recruit neutrophils from the blood to eliminate the bacteria before establishment of infection. To test this hypothesis, two quarters of each of nine healthy cows were challenged with either 50 CFU of E. coli plus saline or 50 CFU of E. coli plus 100 microg of rbosCD14. Quarters challenged with E. coli plus rbosCD14 had a more rapid recruitment of neutrophils, which was accompanied by a faster clearance of bacteria, lower concentrations of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-8 in milk, and milder clinical symptoms, than challenged quarters injected with saline. Results indicate that increasing the concentration of sCD14 in milk may be a potential strategy with which to prevent or reduce the severity of infection by coliform bacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson, J. C. 1978. The effect of colonization of the mouse mammary gland by Staphylococcus epidermidis on subsequent infection with Staphylococcus aureus or Escherichia coli. J. Comp. Pathol. 88:545-553. - PubMed
-
- Bazil, V., V. Horejsi, M. Baudys, H. Kristofova, J. L. Strominger, W. Kostka, and I. Hilgert. 1986. Biochemical characterization of a soluble form of the 53-kDa monocyte surface antigen. Eur. J. Immunol. 16:1583-1589. - PubMed
-
- Bazil, V., and J. L. Strominger. 1991. Shedding as a mechanism of down-modulation of CD14 on stimulated human monocytes. J. Immunol. 147:1567-1574. - PubMed
-
- Bramley, A. J. 1976. Variation in the susceptibility of lactating and non-lactating bovine udders to infection when infused with Escherichia coli. J. Dairy Sci. 79:3094-3103. - PubMed
-
- Burvenich, C., M. J. Paape, A. W. Hill, A. J. Guidry, R. H. Miller, R. Heyneman, W. D. Kremer, and A. Brand. 1994. Role of the neutrophil leukocyte in the local and systemic reactions during experimentally induced E. coli mastitis in cows immediately after calving. Vet. Q. 16:45-50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

