A Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium translocated leucine-rich repeat effector protein inhibits NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression
- PMID: 12819095
- PMCID: PMC162009
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.7.4052-4058.2003
A Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium translocated leucine-rich repeat effector protein inhibits NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression
Abstract
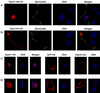
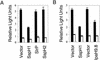
Nontyphoidal salmonellae are enteric pathogens that cause acute gastroenteritis and colonize the intestinal tract for prolonged periods. In the intestinal epithelia, these bacteria induce secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-8 (IL-8), which leads to a profound inflammatory response through recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Production of IL-8 induced by Salmonella spp. is due to the activation of the transcription factors nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) and activator protein-1 (AP-1). This work demonstrates that Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium can downmodulate IL-8 production after invasion of intestinal epithelial cells. The Salmonella translocated effector proteins SspH1 and SptP participate in this process. SspH1 is a member of the bacterial LPX repeat protein family that localizes to the mammalian nucleus and inhibits NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression. A Shigella flexneri translocated effector, IpaH9.8, which has a similar structure and subcellular localization in mammalian cells, also inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. We propose that suppression of inflammatory responses by intracellular S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, and perhaps Shigella flexneri, contributes to bacterial colonization of host tissues and pathogenesis.
Figures
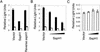
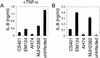
References
-
- Arnold, J. W., D. W. Niesel, C. R. Annable, C. B. Hess, M. Asuncion, Y. J. Cho, J. W. Peterson, and G. R. Klimpel. 1993. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates the early pathology in Salmonella infection of the gastrointestinal tract. Microb. Pathog. 14:217-227. - PubMed
-
- Buchwald, D. S., and M. J. Blaser. 1984. A review of human salmonellosis. II. Duration of excretion following infection with non-typhi Salmonella. Rev. Infect. Dis. 6:345-356. - PubMed
-
- Collier-Hyams, L. S., H. Zeng, J. Sun, A. D. Tomlinson, Z. Q. Bao, H. Chen, J. L. Madara, K. Orth, and A. S. Neish. 2002. Cutting edge: Salmonella AvrA effector inhibits the key proinflammatory, anti-apoptotic NF-κB pathway. J. Immunol. 169:2846-2850. - PubMed
-
- Cooper, J. T., D. M. Stroka, C. Brostjan, A. Palmetshofer, F. H. Bach, and C. Ferran. 1996. A20 blocks endothelial cell activation through a NF-κB-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 271:18068-18073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

