Yersinia pestis TonB: role in iron, heme, and hemoprotein utilization
- PMID: 12819108
- PMCID: PMC161968
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.7.4159-4162.2003
Yersinia pestis TonB: role in iron, heme, and hemoprotein utilization
Abstract
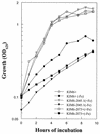
In Yersinia pestis, the siderophore-dependent yersiniabactin (Ybt) iron transport system and heme transport system (Hmu) have putative TonB-dependent outer membrane receptors. Here we demonstrate that hemin uptake and iron utilization from Ybt are TonB dependent. However, the Yfe iron and manganese transport system does not require TonB.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of the hemin uptake locus (hmu) from Yersinia pestis and analysis of hmu mutants for hemin and hemoprotein utilization.Infect Immun. 1999 Aug;67(8):3879-92. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.3879-3892.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10417152 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Haemophilus ducreyi Ton system in internalization of heme from hemoglobin.Infect Immun. 1998 Jan;66(1):151-60. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.1.151-160.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9423852 Free PMC article.
-
TonB-dependent systems of uropathogenic Escherichia coli: aerobactin and heme transport and TonB are required for virulence in the mouse.Infect Immun. 2001 Oct;69(10):6179-85. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.10.6179-6185.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11553558 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial heme sources: the role of heme, hemoprotein receptors and hemophores.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000 Apr;3(2):215-20. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00078-3. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10744995 Review.
-
Heme, an iron supply for vibrios pathogenic for fish.Biometals. 2007 Jun;20(3-4):615-26. doi: 10.1007/s10534-006-9053-8. Epub 2007 Jan 6. Biometals. 2007. PMID: 17206385 Review.
Cited by
-
Modularity analysis based on predicted protein-protein interactions provides new insights into pathogenicity and cellular process of Escherichia coli O157:H7.Theor Biol Med Model. 2011 Dec 22;8:47. doi: 10.1186/1742-4682-8-47. Theor Biol Med Model. 2011. PMID: 22188601 Free PMC article.
-
Shotgun proteomic analysis of Yersinia ruckeri strains under normal and iron-limited conditions.Vet Res. 2016 Oct 6;47(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13567-016-0384-3. Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27716418 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of Yersinia pestis fyuA Mutants Caused by Iron Uptake Inhibition and Decreased Survivability in Macrophages.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 May 4;12:874773. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.874773. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35601093 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of specific in vivo-induced (ivi) genes in Yersinia ruckeri and analysis of ruckerbactin, a catecholate siderophore iron acquisition system.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Sep;70(9):5199-207. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.9.5199-5207.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15345400 Free PMC article.
-
Functional identification of HugZ, a heme oxygenase from Helicobacter pylori.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Dec 17;8:226. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-226. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 19091096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bearden, S. W., and R. D. Perry. 1999. The Yfe system of Yersinia pestis transports iron and manganese and is required for full virulence of plague. Mol. Microbiol. 32:403-414. - PubMed
-
- Braun, V. 1997. Avoidance of iron toxicity through regulation of bacterial iron transport. Biol. Chem. 378:779-786. - PubMed
-
- Deng, W., V. Burland, G. Plunkett III, A. Boutin, G. F. Mayhew, P. Liss, N. T. Perna, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, S. Zhou, D. C. Schwartz, J. D. Fetherston, L. E. Lindler, R. R. Brubaker, G. V. Plano, S. C. Straley, K. A. McDonough, M. L. Nilles, J. S. Matson, F. R. Blattner, and R. D. Perry. 2002. Genome sequence of Yersinia pestis KIM. J. Bacteriol. 184:4601-4611. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fetherston, J. D., S. W. Bearden, and R. D. Perry. 1996. YbtA, an AraC-type regulator of the Yersinia pestis pesticin/yersiniabactin receptor. Mol. Microbiol. 22:315-325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

