Virulence factors and clonal relationships among Escherichia coli strains isolated from broiler chickens with cellulitis
- PMID: 12819112
- PMCID: PMC162012
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.7.4175-4177.2003
Virulence factors and clonal relationships among Escherichia coli strains isolated from broiler chickens with cellulitis
Abstract
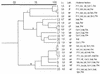
In this study, we compared Escherichia coli isolates from chickens with avian cellulitis with those from feces of healthy chickens. Cellulitis-derived strains presented phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of greater virulence than did the fecal isolates. Phylogenetic analysis by repetitive extragenic palindromic-PCR showed that, in agreement with their virulence characteristics, the cellulitis isolates form two clonal groups distinct from the fecal isolates.
Figures
References
-
- Delicato, E. R., B. G. de Brito, A. P. Konopatzki, L. C. J. Gaziri, and M. C. Vidotto. 2002. Occurrence of the temperature-sensitive hemagglutinin (Tsh) among avian Escherichia coli. Avian Dis. 46:594-601. - PubMed
-
- Fallavena, L. C. B., H. L. S. Moraes, C. T. P. Salle, A. B. da Silva, R. S. Vargas, V. P. do Nascimento, and C. W. Canal. 2000. Diagnosis of skin lesions in condemned or downgraded broiler carcasses—amicroscopic and macroscopic study. Avian Pathol. 29:557-562. - PubMed
-
- Gross, W. B. 1994. Diseases due to Escherichia coli in poultry, p. 237-259. In C. L. Gyles (ed.), Escherichia coli in domestic animals and humans. CAB International, Wallingford, United Kingdom.
-
- Johnson, J. R., and A. L. Stell. 2000. Extended virulence genotypes of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urosepsis in relation to phylogeny and host compromise. J. Infect. Dis. 181:261-272. - PubMed
-
- Moura, A. C., K. Irino, and M. C. Vidotto. 2001. Genetic variability of avian Escherichia coli strains evaluated by enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus and repetitive extragenic palindromic polymerase chain reaction. Avian Dis. 45:173-181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

