Antisense transcripts with FANTOM2 clone set and their implications for gene regulation
- PMID: 12819130
- PMCID: PMC403655
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.982903
Antisense transcripts with FANTOM2 clone set and their implications for gene regulation
Abstract
We have used the FANTOM2 mouse cDNA set (60,770 clones), public mRNA data, and mouse genome sequence data to identify 2481 pairs of sense-antisense transcripts and 899 further pairs of nonantisense bidirectional transcription based upon genomic mapping. The analysis greatly expands the number of known examples of sense-antisense transcript and nonantisense bidirectional transcription pairs in mammals. The FANTOM2 cDNA set appears to contain substantially large numbers of noncoding transcripts suitable for antisense transcript analysis. The average proportion of loci encoding sense-antisense transcript and nonantisense bidirectional transcription pairs on autosomes was 15.1 and 5.4%, respectively. Those on the X chromosome were 6.3 and 4.2%, respectively. Sense-antisense transcript pairs, rather than nonantisense bidirectional transcription pairs, may be less prevalent on the X chromosome, possibly due to X chromosome inactivation. Sense and antisense transcripts tended to be isolated from the same libraries, where nonantisense bidirectional transcription pairs were not apparently coregulated. The existence of large numbers of natural antisense transcripts implies that the regulation of gene expression by antisense transcripts is more common that previously recognized. The viewer showing mapping patterns of sense-antisense transcript pairs and nonantisense bidirectional transcription pairs on the genome and other related statistical data is available on our Web site.
Figures

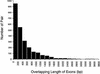


References
-
- Albrecht, U., Sutcliffe, J.S., Cattanach, B.M., Beechey, C.V., Armstrong, D., Eichele, G., and Beaudet, A.L. 1997. Imprinted expression of the murine Angelman syndrome gene, Ube3a, in hippocampal and Purkinje neurons. Nat. Genet. 17: 75-78. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., and Lipman, D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403-410. - PubMed
-
- Andria, M.L., Hsieh, C.L., Oren, R., Francke, U., and Levy, S. 1991. Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the TAPA-1 gene. Immunology 147: 1030-1036. - PubMed
-
- Aravin, A.A., Naumova, N.M., Tulin, A.V., Vagin, V.V., Rozovsky, Y.M., and Gvozdev, V.A. 2001. Double-stranded RNA-mediated silencing of genomic tandem repeats and transposable elements in the D. melanogaster germline. Curr. Biol. 11: 1017-1027. - PubMed
-
- Argaman, L., Hershberg, R., Vogel, J., Bejerano, G., Wagner, E.G., Margalit, H., and Altuvia, S. 2001. Novel small RNA-encoding genes in the intergenic regions of Escherichia coli. Curr. Biol. 11: 941-950. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://fantom2.gsc.riken.go.jp/db/; FANTOM2 database Web site.
-
- http://ftp.genome.washington.edu/RM/RepeatMasker.html; RepeatMasker Web site.
-
- http://genome.gsc.riken.go.jp/m/antisense/; Entrance of the data for this article.
-
- http://genome.gsc.riken.go.jp/m/antisense/imprinted_genes/; list of sense–antisense transcript/transcription mapped +/- 5Mb region of known imprinted genes.
-
- http://genome.gsc.riken.go.jp/m/antisense/viewer/; Entrance of antisense viewer of this article.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
