Discovery of imprinted transcripts in the mouse transcriptome using large-scale expression profiling
- PMID: 12819139
- PMCID: PMC403673
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1055303
Discovery of imprinted transcripts in the mouse transcriptome using large-scale expression profiling
Abstract
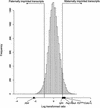
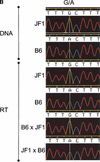
Candidate imprinted transcriptional units in the mouse genome were identified systematically from 27,663 FANTOM2 full-length mouse cDNA clones by expression profiling. Large-scale cDNA microarrays were used to detect differential expression dependent upon chromosomal parent of origin by comparing the mRNA levels in the total tissue of 9.5 dpc parthenogenote and androgenote mouse embryos. Of the FANTOM2 transcripts, 2114 were identified as candidates on the basis of the array data. Of these, 39 mapped to known imprinted regions of the mouse genome, 56 were considered as nonprotein-coding RNAs, and 159 were natural antisense transcripts. The imprinted expression of two transcripts located in the mouse chromosomal region syntenic to the human Prader-Willi syndrome region was confirmed experimentally. We further mapped all candidate imprinted transcripts to the mouse and human genome and were shown in correlation with the imprinting disease loci. These data provide a major resource for understanding the role of imprinting in mammalian inherited traits.
Figures




References
-
- Bielinska, B., Blaydes, S.M., Buiting, K., Yang, T., Krajewska-Walasek, M., Horsthemke, B., and Brannan, C.I. 2000. De novo deletions of SNRPN exon 1 in early human and mouse embryos result in a paternal to maternal imprint switch. Nat. Genet. 25: 74-78. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff, N. 2002. X-chromosome inactivation: Closing in on proteins that bind Xist RNA. Trends Genet. 18: 352-358. - PubMed
-
- Carninci, P., Kvam, C., Kitamura, A., Ohsumi, T., Okazaki, Y., Itoh, M., Kamiya, M., Shibata, K., Sasaki, N., Izawa, M., et al. 1996. High-efficiency full-length cDNA cloning by biotinylated CAP trapper. Genomics 37: 327-336. - PubMed
-
- Collins, F.S. 1995. Positional cloning moves from perditional to traditional. Nat. Genet. 9: 347-350. - PubMed
-
- Deltour, L., Montagutelli, X., Guenet, J.L., Jami, J., and Paldi, A. 1995. Tissue- and developmental stage-specific imprinting of the mouse proinsulin gene, Ins2. Dev. Biol. 168: 686-688. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://www.mgu.har.mrc.ac.uk/imprinting/all_impmaps.html; Imprinting maps, Medical Research Council, Mammalian Genetics Unit, Harwell, UK.
-
- http://fantom2.gsc.riken.go.jp/imprinting/; Candidate imprinted transcripts by expression (CITE) database.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
