Effects of gestational age and prenatal and perinatal events on the coagulation status in premature infants
- PMID: 12819166
- PMCID: PMC1721592
- DOI: 10.1136/fn.88.4.f319
Effects of gestational age and prenatal and perinatal events on the coagulation status in premature infants
Abstract
Objective: To study prospectively the effects of prematurity and perinatal events on the coagulation status of premature infants.
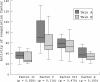
Patients and main outcome measures: Blood samples from premature infants born before 37 gestational weeks were taken for analysis of coagulation factors II, V, VII, and X and platelet count.
Results: A total of 125 premature infants, 71 boys, were studied at the median postnatal age of 40 minutes (range 12-100). The lowest median activities of coagulation factors II, V, VII, and X and the platelet count were observed, as expected, in infants (n = 21) born at 24-27 weeks gestation. Twin B (n = 14) had lower median activities of coagulation factors II, V, VII, and X than twin A. Infants with evidence of mild asphyxia (Apgar score at 5 minutes < 7 or cord pH < 7.26) had significantly (p < 0.05) lower levels of coagulation factors II, V, VII, and X and platelet counts than infants without asphyxia. Infants who were small for gestational age (SGA) had significantly (p < 0.05) lower levels of coagulation factors V and VII and platelet counts than infants of appropriate size for gestational age. Other prenatal and perinatal variables examined (sex, maternal hypertension and/or pre-eclampsia, antenatal steroid use, mode of delivery, Apgar scores) did not show any significant associations with coagulation status, which may be explained by the small number of infants studied.
Conclusions: The data strongly suggest that there are distinct differences in specific coagulation tests in different patient populations, which could assist in the identification of extremely preterm, SGA, or asphyxiated preterm infants who may be susceptible to haemorrhagic problems perinatally.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical