A fuzzy-based histogram analysis technique for skin lesion discrimination in dermatology clinical images
- PMID: 12821032
- PMCID: PMC3184460
- DOI: 10.1016/s0895-6111(03)00030-2
A fuzzy-based histogram analysis technique for skin lesion discrimination in dermatology clinical images
Abstract
A fuzzy logic-based color histogram analysis technique is presented for discriminating benign skin lesions from malignant melanomas in dermatology clinical images. The approach utilizes a fuzzy set for benign skin lesion color, and alpha-cut and support set cardinality for quantifying a fuzzy ratio skin lesion color feature. Skin lesion discrimination results are reported for the fuzzy ratio and fusion with a previously determined percent melanoma color feature over a data set of 258 clinical images. For the fusion technique, alpha-cuts for the fuzzy ratio can be chosen to recognize over 93.30% of melanomas with approximately 15.67% false positive lesions.
Figures
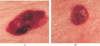
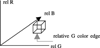

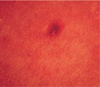
References
-
- Lightstone AC, Kopf AW, Garfinkel L. Diagnostic accuracy—a new approach to its evaluation. Arch Dermatol. 1965;91:497–502. - PubMed
-
- Grin C, Kopf AW, Welkovich B, Bar R, Levenstein M. Diagnostic accuracy in malignant melanoma. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:763–766. - PubMed
-
- Lindelof B, Hedblad MA. Accuracy in the clinical diagnosis and pattern of malignant melanoma at a dermatological clinic. J Dermatol. 1994;21(7):461–464. - PubMed
-
- Friedman RJ, Rigel DS, Kopf AW. Early detection of malignant melanoma: the role of physician examination and self-examination of the skin. Ca—A Cancer J Clinicians. 1985;35(3):130–151. - PubMed
-
- Kopf A, Mintzis M, Bar R. Diagnostic accuracy in malignant melanoma. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:1291–1292. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

