Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of rifampin in an aerosol infection model of tuberculosis
- PMID: 12821456
- PMCID: PMC161844
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2118-2124.2003
Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of rifampin in an aerosol infection model of tuberculosis
Abstract
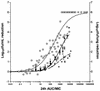
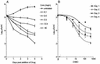
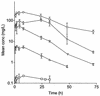
Limited information exists on the pharmacokinetic (PK)-pharmacodynamic (PD) relationships of drugs against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Our aim was to identify the PK-PD parameter that best describes the efficacy of rifampin on the basis of in vitro and PK properties. Consistent with 83.8% protein binding by equilibrium dialysis, the rifampin MIC for M. tuberculosis strain H37Rv rose from 0.1 in a serum-free system to 1.0 mg/ml when it was tested in the presence of 50% serum. In time-kill studies, rifampin exhibited area under the concentration-time curve (AUC)-dependent killing in vitro, with maximal killing seen on all days and with the potency increasing steadily over a 9-day exposure period. MIC and time-kill studies performed with intracellular organisms in a macrophage monolayer model yielded similar results. By use of a murine aerosol infection model with dose ranging and dose fractionation over 6 days, the PD parameter that best correlated with a reduction in bacterial counts was found to be AUC/MIC (r(2) = 0.95), whereas the maximum concentration in serum/MIC (r(2) = 0.86) and the time that the concentration remained above the MIC (r(2) = 0.44) showed lesser degrees of correlation.
Figures
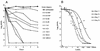
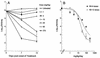
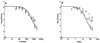
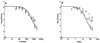
References
-
- Acocella, G., N. A. Carlone, A. M. Cuffini, and G. Cavallo. 1985. The penetration of rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and pyrazinoic acid into mouse macrophages. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 132:1268-1273. - PubMed
-
- Burman, W. J. 1997. The value of in vitro drug activity and pharmacokinetics in predicting the effectiveness of antimycobacterial therapy: a critical review. Am. J. Med. Sci. 31:355-363. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

