Telithromycin- and fluoroquinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in Taiwan with high prevalence of resistance to macrolides and beta-lactams: SMART program 2001 data
- PMID: 12821460
- PMCID: PMC161856
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2145-2151.2003
Telithromycin- and fluoroquinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in Taiwan with high prevalence of resistance to macrolides and beta-lactams: SMART program 2001 data
Abstract
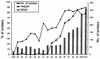
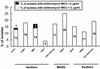
There is a high prevalence of beta-lactam- and macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in Taiwan. To understand the in vitro susceptibilities of recent isolates of S. pneumoniae to fluoroquinolones and telithromycin (which is not available in Taiwan), the MICs of 23 antimicrobial agents for 936 clinical isolates of S. pneumoniae isolated from different parts of Taiwan from 2000 to 2001 were determined by the agar dilution method. Overall, 72% of isolates were not susceptible to penicillin (with 61% being intermediate and 11% being resistant) and 92% were resistant to erythromycin. Telithromycin MICs were >or=1 microg/ml for 16% of the isolates, and for 99% of these isolates the MICs of all macrolides tested were >or=256 microg/ml; all of these isolates had the constitutive macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B phenotype. Eighty-eight percent of the isolates were resistant to three or more classes of drugs. The ciprofloxacin MICs were >or=4 microg/ml for six (0.6%) isolates from five patients collected in 2000 and 2001, and the levofloxacin MICs were >or=8 microg/ml for five of these isolates. Seven isolates for which ciprofloxacin MICs were >or=4 microg/ml, including one isolate recovered in 1999, belonged to three serotypes (serotype 19F, five isolates; serotype 23A, one isolate; and serotype 23B, one isolate). The isolates from the six patients for which ciprofloxacin MICs were >or=4 microg/ml had different pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles and random amplified polymorphic DNA patterns, indicating that no clonal dissemination occurred over this time period. Despite the increased rate of fluoroquinolone use, the proportion of pneumococcal isolates for which ciprofloxacin MICs were elevated (>or=4 microg/ml) remained low. However, the occurrence of telithromycin resistance is impressive and raises concerns for the future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Telithromycin and quinupristin-dalfopristin resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes: SMART Program 2001 Data.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Jul;47(7):2152-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2152-2157.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12821461 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibilities to telithromycin and six other agents and prevalence of macrolide resistance due to L4 ribosomal protein mutation among 992 Pneumococci from 10 central and Eastern European countries.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Feb;46(2):371-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.2.371-377.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 11796344 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of telithromycin against Spanish Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates with characterized macrolide resistance mechanisms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Sep;45(9):2427-31. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.9.2427-2431.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11502509 Free PMC article.
-
Regional trends in beta-lactam, macrolide, fluoroquinolone and telithromycin resistance among Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates 2001-2004.J Infect. 2007 Aug;55(2):111-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2007.04.006. Epub 2007 Jun 12. J Infect. 2007. PMID: 17568680 Review.
-
Multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae infections: current and future therapeutic options.Drugs. 2007;67(16):2355-82. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767160-00005. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17983256 Review.
Cited by
-
Superiority of D-zone Testing Method over Standard Method to detect Rnducible Resistance in Gram Positive Bacteria: a Prospective Surveillance from a Teaching Hospital in Saudi Arabia.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2008 Jul;2(2):8-16. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2008. PMID: 21475484 Free PMC article.
-
Update of practice guidelines for the management of community-acquired pneumonia in immunocompetent adults.Clin Infect Dis. 2003 Dec 1;37(11):1405-33. doi: 10.1086/380488. Epub 2003 Nov 3. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 14614663 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Portugal over an 11-year period.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jun;50(6):2098-105. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00198-06. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16723571 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activities of oral cephem and telithromycin against clinical isolates of major respiratory pathogens in Japan.J Korean Med Sci. 2007 Feb;22(1):20-5. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.20. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17297246 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal spread of highly beta-lactam-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Taiwan.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Jun;52(6):2266-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00046-08. Epub 2008 Apr 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18413298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang, S. C., Y. C. Chen, and O. Y. P. Hu. 2001. Antibiotic use in public hospitals in Taiwan after the implementation of National Health Insurance. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 100:151-161. - PubMed
-
- Chen, D. K., A. McGeer, J. C. De Azavedo, and D. E. Low for the Canadian Bacterial Surveillance Network. 1999. Decreased susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae to fluoroquinolones in Canada. N. Engl. J. Med. 341:233-239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

