Effect of calcium carbonate on bioavailability of orally administered gemifloxacin
- PMID: 12821462
- PMCID: PMC161830
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2158-2160.2003
Effect of calcium carbonate on bioavailability of orally administered gemifloxacin
Abstract
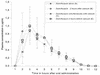
We investigated the effect of calcium carbonate on the oral bioavailability of gemifloxacin. Gemifloxacin was administered alone, 2 h before, simultaneously, or 2 h after calcium carbonate in 16 volunteers. Data for 320 mg of gemifloxacin alone were as follows: maximum concentration of drug in serum (C(max)),13 microg/ml; half-life, 7.33 h; and area under the concentration-time curve from 0 h to infinity (AUC( infinity )), 6.79 microg. h/ml. Only simultaneous coadministration of calcium carbonate reduced C(max) (-17%) and AUC( infinity ) (-21%) significantly.
Figures
References
-
- Aminimanizani, A., P. Beringer, and R. Jelliffe. 2001. Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the newer fluoroquinolone antibacterials. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 40:169-187. - PubMed
-
- Biedenbach, D. J., and R. N. Jones. 2002. Evaluation of in vitro susceptibility testing criteria for gemifloxacin when tested against Haemophilus influenzae strains with reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 43:323-326. - PubMed
-
- Boswell, F. J., J. M. Andrews, G. Jevons, and R. Wise. 2002. Comparison of the in vitro activities of several new fluoroquinolones against respiratory pathogens and their abilities to select fluoroquinolone resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 50:495-502. - PubMed
-
- Dunnett, C. W. 1995. A multiple comparisons procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. J. Am. Statist. Ass. 50:1096-1121.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

