Allele-specific rpoB PCR assays for detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum smears
- PMID: 12821473
- PMCID: PMC161874
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2231-2235.2003
Allele-specific rpoB PCR assays for detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum smears
Abstract
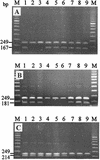
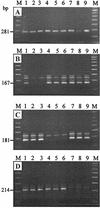
We describe an allele-specific PCR assay to detect mutations in three codons of the rpoB gene (516, 526, and 531) in Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains; mutations in these codons are reported to account for majority of M. tuberculosis clinical isolates resistant to rifampin (RIF), a marker of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Three different allele-specific PCRs are carried out either directly with purified DNA (single-step multiplex allele-specific PCR), or with preamplified rpoB fragment (nested allele-specific PCR [NAS-PCR]). The method was optimized and validated following analysis of 36 strains with known rpoB sequence. A retrospective analysis of the 287 DNA preparations from epidemiologically unlinked RIF-resistant clinical strains from Russia, collected from 1996 to 2002, revealed that 247 (86.1%) of them harbored a mutation in one of the targeted rpoB codons. A prospective study of microscopy-positive consecutive sputum samples from new and chronic TB patients validated the method for direct analysis of DNA extracted from sputum smears. The potential of the NAS-PCR to control for false-negative results due to lack of amplification was proven especially useful in the study of these samples. The developed rpoB-PCR assay can be used in clinical laboratories to detect RIF-resistant and hence MDR M. tuberculosis in the regions with high burdens of the MDR-TB.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The New Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra: Improving Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Resistance to Rifampin in an Assay Suitable for Point-of-Care Testing.mBio. 2017 Aug 29;8(4):e00812-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00812-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28851844 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid detection of smear-negative Mycobacterium tuberculosis by PCR and sequencing for rifampin resistance with DNA extracted directly from slides.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Jan;39(1):51-2. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.1.51-52.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11136747 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of efficiency of nested multiplex allele-specific PCR assay for detection of multidrug resistant tuberculosis directly from sputum samples.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016 May;62(5):411-8. doi: 10.1111/lam.12564. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26972777
-
Mutations inside rifampicin-resistance determining region of rpoB gene associated with rifampicin-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Infect Public Health. 2018 Sep-Oct;11(5):605-610. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 26. J Infect Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29706316 Review.
-
The overview and perspectives of biosensors and Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A systematic review.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Mar;236(3):1730-1750. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30007. Epub 2020 Sep 15. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32930412
Cited by
-
Rifampicin-Resistance Mutations in the rpoB Gene in Bacillus velezensis CC09 have Pleiotropic Effects.Front Microbiol. 2017 Feb 13;8:178. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00178. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28243227 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis by high-throughput sequencing of DNA isolated from acid fast bacilli smears.PLoS One. 2020 May 8;15(5):e0232343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232343. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32384098 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Isoniazid-, Fluoroquinolone-, Amikacin-, and Kanamycin-Resistant Tuberculosis in an Automated, Multiplexed 10-Color Assay Suitable for Point-of-Care Use.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 Dec 28;55(1):183-198. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01771-16. Print 2017 Jan. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27807153 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex detection of extensively drug resistant tuberculosis using binary deoxyribozyme sensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Aug 15;94:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.02.051. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 28284077 Free PMC article.
-
Isoniazid and rifampin drug susceptibility testing: application of 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride assay and microscopic-observation drug-susceptibility assay directly on Ziehl-Neelsen smear positive sputum specimens.Braz J Infect Dis. 2016 Jan-Feb;20(1):33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Braz J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26638012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartfai, Z., A. Somoskovi, C. Kodmon, N. Szabo, E. Puskas, L. Kosztolanyi, E. Farago, J. Mester, L. M. Parsons, and M. Salfinger. 2001. Molecular characterization of rifampin-resistant isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from Hungary by DNA sequencing and the line probe assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:3736-3739. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dragon, E. A., J. P. Spadoro, and R. Madej. 1993. Quality control of polymerase chain reaction, p. 160-168. In D. H. Persing, T. F. Smith, F. C. Tenover, and T. J. White (ed.), Diagnostic molecular microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

