A network of transcriptional and signaling events is activated by FGF to induce chondrocyte growth arrest and differentiation
- PMID: 12821644
- PMCID: PMC2172997
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200302075
A network of transcriptional and signaling events is activated by FGF to induce chondrocyte growth arrest and differentiation
Abstract
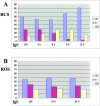
Activating mutations in FGF receptor 3 (FGFR3) cause several human dwarfism syndromes by affecting both chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Using microarray and biochemical analyses of FGF-treated rat chondrosarcoma chondrocytes, we show that FGF inhibits chondrocyte proliferation by initiating multiple pathways that result in the induction of antiproliferative functions and the down-regulation of growth-promoting molecules. The initiation of growth arrest is characterized by the rapid dephosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) p107 and repression of a subset of E2F target genes by a mechanism that is independent of cyclin E-Cdk inhibition. In contrast, hypophosphorylation of pRb and p130 occur after growth arrest is first detected, and may contribute to its maintenance. Importantly, we also find a number of gene expression changes indicating that FGF promotes many aspects of hypertrophic differentiation, a notion supported by in situ analysis of developing growth plates from mice expressing an activated form of FGFR3. Thus, FGF may coordinate the onset of differentiation with chondrocyte growth arrest in the developing growth plate.
Figures





References
-
- Aikawa, T., G.V. Segre, and K. Lee. 2001. Fibroblast growth factor inhibits chondrocytic growth through induction of p21 and subsequent inactivation of cyclin E-Cdk2. J. Biol. Chem. 276:29347–29352. - PubMed
-
- Brugarolas, J., C. Chandrasekaran, J.I. Gordon, D. Beach, T. Jacks, and G.J. Hannon. 1995. Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 377:552–557. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C.R., Y. Kang, P.M. Siegel, and J. Massague. 2002. E2F4/5 and p107 as Smad cofactors linking the TGFbeta receptor to c-myc repression. Cell. 110:19–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

