Back signaling by the Nrg-1 intracellular domain
- PMID: 12821646
- PMCID: PMC2172983
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200212085
Back signaling by the Nrg-1 intracellular domain
Abstract
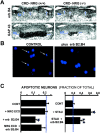
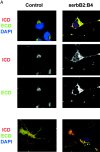
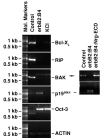
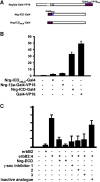
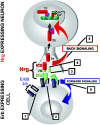
Transmembrane isoforms of neuregulin-1 (Nrg-1), ligands for erbB receptors, include an extracellular domain with an EGF-like sequence and a highly conserved intracellular domain (ICD) of unknown function. In this paper, we demonstrate that transmembrane isoforms of Nrg-1 are bidirectional signaling molecules in neurons. The stimuli for Nrg-1 back signaling include binding of erbB receptor dimers to the extracellular domain of Nrg-1 and neuronal depolarization. These stimuli elicit proteolytic release and translocation of the ICD of Nrg-1 to the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, the Nrg-1 ICD represses expression of several regulators of apoptosis, resulting in decreased neuronal cell death in vitro. Thus, regulated proteolytic processing of Nrg-1 results in retrograde signaling that appears to mediate contact and activity-dependent survival of Nrg-1-expressing neurons.
Figures




References
-
- Aguilar, Z., and D.J. Slamon. 2001. The transmembrane heregulin precursor is functionally active. J. Biol. Chem. 276:44099–44107. - PubMed
-
- Aizawa, H., S. Wakatsuki, A. Ishii, K. Moriyama, Y. Sasaki, K. Ohashi, Y. Sekine-Aizawa, A. Sehara-Fujisawa, K. Mizuno, Y. Goshima, and I. Yahara. 2001. Phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase is necessary for semaphorin 3A-induced growth cone collapse. Nat. Neurosci. 4:367–373. - PubMed
-
- Arber, S., F.A. Barbayannis, H. Hanser, C. Schneider, C.A. Stanyon, O. Bernard, and P. Caroni. 1998. Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature. 393:805–809. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M.S., and J.L. Goldstein. 1997. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 89:331–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

