Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II potentiates store-operated Ca2+ current
- PMID: 12821654
- PMCID: PMC1282465
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M305023200
Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II potentiates store-operated Ca2+ current
Abstract
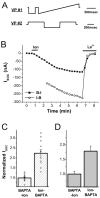
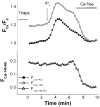
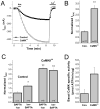
A rise in intracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+i) mediates various cellular functions ranging from fertilization to gene expression. A ubiquitous Ca2+ influx pathway that contributes significantly to the generation of Ca2+i signals, especially in non-excitable cells, is store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE). Consequently, the modulation of SOCE current affects Ca2+i dynamics and thus the ensuing cellular response. Therefore, it is important to define the mechanisms that regulate SOCE. Here we show that a rise in Ca2+i potentiates SOCE. This potentiation is mediated by Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), because inhibition of endogenous CaMKII activity abrogates Ca2+i-mediated SOCE potentiation and expression of constitutively active CaMKII potentiates SOCE current independently of Ca2+i. Moreover, we present evidence that CaMKII potentiates SOCE by altering SOCE channel gating. The regulation of SOCE by CaMKII defines a novel modulatory mechanism of SOCE with important physiological consequences.
Figures

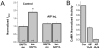
Similar articles
-
CaMKII Potentiates Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry Through Enhancing STIM1 Aggregation and Interaction with Orai1.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(3):1042-1054. doi: 10.1159/000488835. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29669320
-
Involvement of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II pathway in the Ca2+-mediated regulation of the capacitative Ca2+ entry in Xenopus oocytes.Biochem J. 1997 Feb 15;322 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):267-72. doi: 10.1042/bj3220267. Biochem J. 1997. PMID: 9078272 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII tethers to L-type Ca2+ channels, establishing a local and dedicated integrator of Ca2+ signals for facilitation.J Cell Biol. 2005 Nov 7;171(3):537-47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200505155. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16275756 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Disorders and Cancer: Hepatocyte Store-Operated Ca2+ Channels in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;993:595-621. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-57732-6_30. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28900935 Review.
-
Calmodulin and CaMKII as molecular switches for cardiac ion channels.Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Mar 1;73(4):641-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.10.019. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17137569 Review.
Cited by
-
Gravitational force modulates G2/M phase exit in mechanically unloaded myoblasts.Cell Cycle. 2013 Sep 15;12(18):3001-12. doi: 10.4161/cc.26029. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23974110 Free PMC article.
-
CRAC channel activity in C. elegans is mediated by Orai1 and STIM1 homologues and is essential for ovulation and fertility.J Physiol. 2007 Apr 1;580(Pt 1):67-85. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.124883. Epub 2007 Jan 11. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17218360 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological roles of STIM1 and Orai1 homologs and CRAC channels in the genetic model organism Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Calcium. 2007 Aug;42(2):193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Cell Calcium. 2007. PMID: 17376526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual effect of calmodulin on store-operated Ca2+ -permeable cation channels in rabbit portal vein myocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;148(7):1001-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706797. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16770321 Free PMC article.
-
Function of a STIM1 homologue in C. elegans: evidence that store-operated Ca2+ entry is not essential for oscillatory Ca2+ signaling and ER Ca2+ homeostasis.J Gen Physiol. 2006 Oct;128(4):443-59. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200609611. Epub 2006 Sep 11. J Gen Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16966474 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

