Matrix metalloproteinase expression in the olfactory epithelium
- PMID: 12821796
- PMCID: PMC2717620
- DOI: 10.1097/00001756-200306110-00007
Matrix metalloproteinase expression in the olfactory epithelium
Abstract
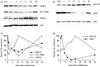
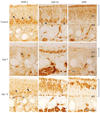
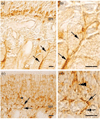
The olfactory epithelium contains neuronal progenitor cells capable of continuous neurogenesis and is a unique model for studying neural degeneration, regeneration, axon outgrowth and recovery from injury. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), have been implicated in cell turnover, development, migration, and metastatic processes. We used Western blot and immunohistochemistry to determine whether MMP-2 and associated proteins TIMP-2 and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) are present in the olfactory epithelium of mice. We found MMP-2 expression localized to the olfactory basal cells and immature neurons. After injury-induced neural degeneration, MMP-2 and MT1-MMP levels decreased while TIMP-2 levels increased. However, following 35 days of neurogenesis and cell replacement TIMP-2 and MT1-MMP returned to control levels. The results show a correlation between MMP and TIMP levels and the stages of neural degeneration, regeneration and recovery of the olfactory epithelium following injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and its co-localization with membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) correlate with melanoma progression.J Pathol. 2000 Jul;191(3):245-56. doi: 10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH632>3.0.CO;2-#. J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10878545
-
Matrix metalloproteinase expression and function during fin regeneration in zebrafish: analysis of MT1-MMP, MMP2 and TIMP2.Matrix Biol. 2005 Jun;24(4):247-60. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2005.03.007. Matrix Biol. 2005. PMID: 15935631
-
Analysis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 effect on pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 activation by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase using baculovirus/insect-cell expression system.Biochem J. 2000 Feb 1;345 Pt 3(Pt 3):511-9. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10642509 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking and secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in olfactory ensheathing glial cells: A role in cell migration?Glia. 2011 May;59(5):750-70. doi: 10.1002/glia.21146. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21360755
-
Expression of integrin alpha(v)beta(3) correlates with activation of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in human melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Int J Cancer. 2000 Jul 1;87(1):12-9. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(20000701)87:1<12::aid-ijc3>3.0.co;2-a. Int J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10861447
Cited by
-
Matrix rigidity activates Wnt signaling through down-regulation of Dickkopf-1 protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 4;288(1):141-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.431411. Epub 2012 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23152495 Free PMC article.
-
Mild Fluid Percussion Injury Induces Diffuse Axonal Damage and Reactive Synaptic Plasticity in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb.Neuroscience. 2018 Feb 10;371:106-118. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.11.045. Epub 2017 Dec 2. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29203228 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of metalloproteinases in neurogenesis in the gerbil hippocampus following global forebrain ischemia.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022465. Epub 2011 Jul 25. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799862 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Lived Human Umbilical Cord-Blood-Derived Neural Stem Cells Influence the Endogenous Secretome and Increase the Number of Endogenous Neural Progenitors in a Rat Model of Lacunar Stroke.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6413-6425. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9530-6. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26607630 Free PMC article.
-
Time dependent integration of matrix metalloproteinases and their targeted substrates directs axonal sprouting and synaptogenesis following central nervous system injury.Neural Regen Res. 2014 Feb 15;9(4):362-76. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.128237. Neural Regen Res. 2014. PMID: 25206824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costanzo RM. Ciba Found Symp. 1991;160:233–242. - PubMed
-
- Calof AL, Mumm JS, Rim PC, et al. J Neurobiol. 1998;36:190–205. - PubMed
-
- Graziadei PPC, Monti Graziadei GA. Am J Otolaryngol. 1983;4:228–233. - PubMed
-
- Holbrook EH, Szumowski KE, Schwob JE. J Comp Neurol. 1995;363:129–146. - PubMed
-
- Schwob JE. Anat Rec. 2002;269:33–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

