Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction
- PMID: 12824337
- PMCID: PMC169194
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg595
Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction
Abstract
The abbreviated name, 'mfold web server', describes a number of closely related software applications available on the World Wide Web (WWW) for the prediction of the secondary structure of single stranded nucleic acids. The objective of this web server is to provide easy access to RNA and DNA folding and hybridization software to the scientific community at large. By making use of universally available web GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces), the server circumvents the problem of portability of this software. Detailed output, in the form of structure plots with or without reliability information, single strand frequency plots and 'energy dot plots', are available for the folding of single sequences. A variety of 'bulk' servers give less information, but in a shorter time and for up to hundreds of sequences at once. The portal for the mfold web server is http://www.bioinfo.rpi.edu/applications/mfold. This URL will be referred to as 'MFOLDROOT'.
Figures

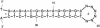
References
-
- Fresco J.R., Alberts,B.M. and Doty,P. (1960) Some molecular details of the secondary structure of ribonucleic acid. Nature, 188, 98–101. - PubMed
-
- Borer P.N., Dengler,B., Tinoco,I.,Jr and Uhlenbeck,O.C. (1974) Stability of ribonucleic acid double-stranded helices. J. Mol. Biol., 86, 843–853. - PubMed
-
- Tinoco I., Jr and Uhlenbeck,O.C. (1971) Estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature, 230, 362–367. - PubMed
-
- Tinoco I. Jr, Borer,P.N., Dengler,B., Levine,M.D., Uhlenbeck,O.C., Crothers,D.M. and Gralla,J. (1973) Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature New Biol., 246, 40–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

