mreps: Efficient and flexible detection of tandem repeats in DNA
- PMID: 12824391
- PMCID: PMC169196
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg617
mreps: Efficient and flexible detection of tandem repeats in DNA
Abstract
The presence of repeated sequences is a fundamental feature of genomes. Tandemly repeated DNA appears in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic genomes, it is associated with various regulatory mechanisms and plays an important role in genomic fingerprinting. In this paper, we describe mreps, a powerful software tool for a fast identification of tandemly repeated structures in DNA sequences. mreps is able to identify all types of tandem repeats within a single run on a whole genomic sequence. It has a resolution parameter that allows the program to identify 'fuzzy' repeats. We introduce main algorithmic solutions behind mreps, describe its usage, give some execution time benchmarks and present several case studies to illustrate its capabilities. The mreps web interface is accessible through http://www.loria.fr/mreps/.
Figures

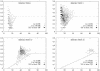
References
-
- Brown T.A. (1999) Genomes. BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford, UK.
-
- Richards R.I., Holman,K., Yu,S. and Sutherland,G.R. (1993) Fragile X syndrome unstable element, p(CCG)n, and other simple tandem repeat sequences are binding sites for specific nuclear proteins. Hum. Mol. Genet., 2, 1429–1435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

