Mechanisms of selectivity in channels and enzymes studied with interactive molecular dynamics
- PMID: 12829462
- PMCID: PMC1303063
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74452-X
Mechanisms of selectivity in channels and enzymes studied with interactive molecular dynamics
Abstract
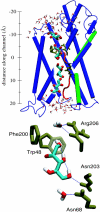
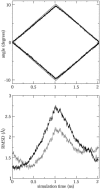
Interactive molecular dynamics, a new modeling tool for rapid investigation of the physical mechanisms of biological processes at the atomic level, is applied to study selectivity and regulation of the membrane channel protein GlpF and the enzyme glycerol kinase. These proteins facilitate the first two steps of Escherichia coli glycerol metabolism. Despite their different function and architecture the proteins are found to employ common mechanisms for substrate selectivity: an induced geometrical fit by structurally homologous binding sites and an induced rapid dipole moment reversal. Competition for hydrogen bonding sites with water in both proteins is critical for substrate motion. In glycerol kinase, it is shown that the proposed domain motion prevents competition with water, in turn regulating the binding of glycerol.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Engineering teams up with computer-simulation and visualization tools to probe biomolecular mechanisms.Biophys J. 2003 Jul;85(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74448-8. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 12829458 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Water and glycerol permeation through the glycerol channel GlpF and the aquaporin family.J Synchrotron Radiat. 2004 Jan 1;11(Pt 1):86-8. doi: 10.1107/s0909049503023872. Epub 2003 Nov 28. J Synchrotron Radiat. 2004. PMID: 14646142 Review.
-
Glycerol conductance and physical asymmetry of the Escherichia coli glycerol facilitator GlpF.Biophys J. 2003 Nov;85(5):2977-87. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74718-3. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 14581200 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion of glycerol through Escherichia coli aquaglyceroporin GlpF.Biophys J. 2008 Feb 1;94(3):832-9. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.115105. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 17921212 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic structure of a glycerol channel and implications for substrate permeation in aqua(glycero)porins.FEBS Lett. 2001 Aug 31;504(3):112-7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02710-7. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11532442 Review.
Cited by
-
Stereochemical errors and their implications for molecular dynamics simulations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 May 23;12:190. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-190. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21605430 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics-based refinement and validation for sub-5 Å cryo-electron microscopy maps.Elife. 2016 Jul 7;5:e16105. doi: 10.7554/eLife.16105. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27383269 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics-based approaches for enhanced sampling of long-time, large-scale conformational changes in biomolecules.F1000 Biol Rep. 2009 Jul 8;1:51. doi: 10.3410/B1-51. F1000 Biol Rep. 2009. PMID: 20948633 Free PMC article.
-
W254 in furin functions as a molecular gate promoting anti-viral drug binding: Elucidation of putative drug tunneling and docking by non-equilibrium molecular dynamics.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Sep 9;21:4589-4612. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.09.003. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37817778 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics simulations of proteins in lipid bilayers.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Aug;15(4):423-31. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.07.007. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 16043343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ai, Z., and T. Fröhlich. 1998. Molecular dynamics simulation in virtual environments. Comp. Graph. Forum. 17:C267–C273.
-
- Borgnia, M., S. Nielsen, A. Engel, and P. Agre. 1999. Cellular and molecular biology of the aquaporin water channels. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68:425–458. - PubMed
-
- Bystrom, C. E., D. W. Pettigrew, B. P. Branchaud, P. O'Brien, and S. J. Remington. 1999. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli glycerol kinase variant S58→W in complex with nonhydrolyzable ATP analogues reveal a putative active conformation of the enzyme as a result of domain motion. Biochemistry. 38:3508–3518. - PubMed
-
- de Groot, B. L., A. Engel, and H. Grubmüller. 2001. A refined structure of human aquaporin-1. FEBS Lett. 504:206–211. - PubMed
-
- de Groot, B. L., and H. Grubmüller. 2001. Water permeation across biological membranes: mechanism and dynamics of aquaporin-1 and GlpF. Science. 294:2353–2357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

