Location of structural transitions in an isotopically labeled lung surfactant SP-B peptide by IRRAS
- PMID: 12829488
- PMCID: PMC1303089
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74478-6
Location of structural transitions in an isotopically labeled lung surfactant SP-B peptide by IRRAS
Abstract
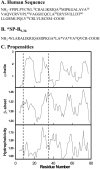
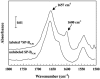
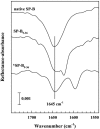
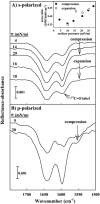
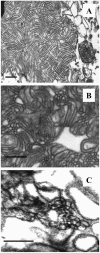
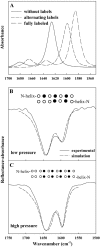
Pulmonary surfactant, a lipid/protein complex that lines the air/water interface in the mammalian lung, functions to reduce the work of breathing. Surfactant protein B (SP-B) is a small, hydrophobic protein that is an essential component of this mixture. Structure-function relationships of SP-B are currently under investigation as the protein and its peptide analogs are being incorporated into surfactant replacement therapies. Knowledge of the structure of SP-B and its related peptides in bulk and monolayer phases will facilitate the design of later generation therapeutic agents. Prior infrared reflection-absorption spectroscopic studies reported notable, reversible surface pressure-induced antiparallel beta-sheet formation in a synthetic peptide derived from human SP-B, residues 9-36 (SP-B(9-36)). In the current work, infrared reflection-absorption spectroscopy is applied in conjunction with isotopic labeling to detect the site and pressure dependence of the conformational change. SP-B(9-36), synthesized with (13)C=O-labeled Ala residues in positions 26, 28, 30, and 32, shifted the beta-sheet marker band to approximately 1600 cm(-1) and thus immediately identified this structural element within the labeled region. Surface pressure-induced alterations in the relative intensities of Amide I band constituents are interpreted using a semiempirical transition dipole coupling model. In addition, electron micrographs reveal the formation of tubular myelin structures from in vitro preparations using SP-B(9-36) in place of porcine SP-B indicating that the peptide has the potential to mimic this property of the native protein.
Figures
References
-
- Andersson, M., T. Curstedt, H. Jornvall, and J. Johansson. 1995. An amphipathic helical motif common to tumourolytic polypeptide NK-lysin and pulmonary surfactant polypeptide SP-B. FEBS Lett. 362:328–332. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett, G. R. 1959. Phosphorous assay in column chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 234:466–468. - PubMed
-
- Bi, X., C. R. Flach, J. Perez-Gil, I. Plasencia, D. Andreu, E. Oliveira, and R. Mendelsohn. 2002. Secondary structure and lipid interactions of the N-terminal segment of pulmonary surfactant SP-C in Langmuir films: IR reflection-absorption spectroscopy and surface pressure studies. Biochemistry. 41:8385–8395. - PubMed
-
- Brauner, J. W., C. Dugan, and R. Mendelsohn. 2000. 13C isotope labeling of hydrophobic peptides. Origin of the anomalous intensity distribution in the infrared Amide I spectral region of β-sheet structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122:677–683.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

