Relative affinity constants by electrospray ionization and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: calmodulin binding to peptide analogs of myosin light chain kinase
- PMID: 12829504
- PMCID: PMC1303105
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74494-4
Relative affinity constants by electrospray ionization and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: calmodulin binding to peptide analogs of myosin light chain kinase
Abstract
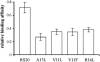
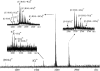
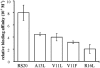
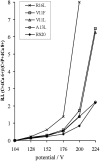
Synthetic RS20 peptide and a set of its point-mutated peptide analogs have been used to analyze the interactions between calmodulin (CaM) and the CaM-binding sequence of smooth-muscle myosin light chain kinase both in the presence and the absence of Ca(2+). Particular peptides, which were expected to have different binding strengths, were chosen to address the effects of electrostatic and bulky mutations on the binding affinity of the RS20 sequence. Relative affinity constants for protein/ligand interactions have been determined using electrospray ionization and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. The results evidence the importance of electrostatic forces in interactions between CaM and targets, particularly in the presence of Ca(2+), and the role of hydrophobic forces in contributing additional stability to the complexes both in the presence and the absence of Ca(2+).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Calmodulin-peptide interactions: apocalmodulin binding to the myosin light chain kinase target-site.Biochemistry. 2000 Jun 20;39(24):7284-90. doi: 10.1021/bi000139m. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10852728
-
Mapping protein interfaces by a trifunctional cross-linker combined with MALDI-TOF and ESI-FTICR mass spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005 Dec;16(12):1921-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2005.07.020. Epub 2005 Oct 24. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005. PMID: 16246579
-
Chemical cross-linking and high-performance Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry for protein interaction analysis: application to a calmodulin/target peptide complex.Anal Chem. 2005 Jan 15;77(2):495-503. doi: 10.1021/ac0487294. Anal Chem. 2005. PMID: 15649045
-
Structure, dynamics and interaction with kinase targets: computer simulations of calmodulin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):289-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.032. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023369 Review.
-
Electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry.Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1999;50:517-36. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physchem.50.1.517. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1999. PMID: 10575730 Review.
Cited by
-
The formation of a complex between calmodulin and neuronal nitric oxide synthase is determined by ESI-MS.J R Soc Interface. 2005 Dec 22;2(5):465-76. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2005.0055. J R Soc Interface. 2005. PMID: 16849206 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry studies of noncovalent myosin VI complexes reveal a new specific calmodulin binding site.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005 Aug;16(8):1367-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2005.03.023. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005. PMID: 15979337
-
Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding.Chem Rev. 2008 Mar;108(3):946-1051. doi: 10.1021/cr050262p. Chem Rev. 2008. PMID: 18335973 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Distinct mechanisms of calmodulin binding and regulation of adenylyl cyclases 1 and 8.Biochemistry. 2012 Oct 9;51(40):7917-29. doi: 10.1021/bi300646y. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22971080 Free PMC article.
-
The unique insert in myosin VI is a structural calcium-calmodulin binding site.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 6;101(14):4787-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0306892101. Epub 2004 Mar 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15037754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afshar, M., L. S. D. Caves, L. Guimard, R. E. Hubbard, B. Calas, G. Grassy, and J. Haiech. 1994. Investigating the high affinity and low sequence specificity of calmodulin binding to its targets. J. Mol. Biol. 244:554–571. - PubMed
-
- Babu, Y. S., C. E. Bugg, and W. J. Cook. 1988. Structure of calmodulin refined at 2.2 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 204:191–204. - PubMed
-
- Barth, A., S. R. Martin, and P. M. Bayley. 1998. Specificity and symmetry in the interaction of calmodulin domains with the skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase target sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 273:2174–2183. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyaya, R., W. E. Meador, A. R. Means, and F. A. Quiocho. 1992. Calmodulin structure refined at 1.7 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 228:1177–1192. - PubMed
-
- Craig, T. A., D. M. Watterson, F. G. Prendergast, J. Haiech, and D. M. Roberts. 1987. Site-specific mutagenesis of the alpha-helices of calmodulin. Effects of altering a charge cluster in the helix that links the two halves of calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 262:3278–3284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

