Redox-induced structural dynamics of Fe-heme ligand in myoglobin by X-ray absorption spectroscopy
- PMID: 12829509
- PMCID: PMC1303110
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74499-3
Redox-induced structural dynamics of Fe-heme ligand in myoglobin by X-ray absorption spectroscopy
Abstract
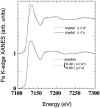
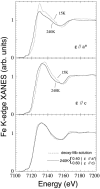
The Fe(III) --> Fe(II) reduction of the heme iron in aquomet-myoglobin, induced by x-rays at cryogenics temperatures, produces a thermally trapped nonequilibrium state in which a water molecule is still bound to the iron. Water dissociates at T > 160 K, when the protein can relax toward its new equilibrium, deoxy form. Synchrotron radiation x-ray absorption spectroscopy provides information on both the redox state and the Fe-heme structure. Owing to the development of a novel method to analyze the low-energy region of x-ray absorption spectroscopy, we obtain structural pictures of this photo-inducible, irreversible process, with 0.02-0.06-A accuracy, on the protein in solution as well as in crystal. After photo-reduction, the iron-proximal histidine bond is shortened by 0.15 A, a reinforcement that should destabilize the iron in-plane position favoring water dissociation. Moreover, we are able to get the distance of the water molecule even after dissociation from the iron, with a 0.16-A statistical error.
Figures





References
-
- Benfatto, M., and S. Della Longa. 2001. Geometrical fitting of experimental XANES spectra by a full multiple scattering procedure. J. Synchrotron Rad. 8:1087–1094. - PubMed
-
- Benfatto, M., P. D'Angelo, S. Della Longa, and N.V. Pavel. 2002. Evidence of distorted fivefold coordination of the Cu2+ aqua ion from an x-ray absorption spectroscopy quantitative analysis. Phys. Rev. B. 65:174205.
-
- Blumenfeld, L. 1981. Problems of Biological Physics. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
-
- Burmeister, W. P. 2000. Structural changes in a cryo-cooled protein crystal owing to radiation damage. Acta Crystallogr. D. 56:328–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

