HIV protease inhibitors acutely impair glucose-stimulated insulin release
- PMID: 12829635
- PMCID: PMC1403824
- DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.52.7.1695
HIV protease inhibitors acutely impair glucose-stimulated insulin release
Abstract
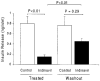
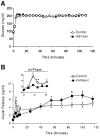
HIV protease inhibitors (PIs) acutely and reversibly inhibit the insulin-responsive glucose transporter Glut 4, leading to peripheral insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance. Minimal modeling analysis of glucose tolerance tests on PI-treated patients has revealed an impaired insulin secretory response, suggesting additional pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. To determine whether beta-cell function is acutely affected by PIs, we assayed glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in rodent islets and the insulinoma cell line MIN6. Insulin release from MIN6 cells and rodent islets was significantly inhibited by the PI indinavir with IC(50) values of 1.1 and 2.1 micro mol/l, respectively. The uptake of 2-deoxyglucose in MIN6 cells was similarly inhibited (IC(50) of 2.0 micro mol/l), whereas glucokinase activity was unaffected at drug levels as high as 1 mmol/l. Glucose utilization was also impaired at comparable drug levels. Insulin secretogogues acting downstream of glucose transport mostly reversed the indinavir-mediated inhibition of insulin release in MIN6 cells. Intravenous infusion of indinavir during hyperglycemic clamps on rats significantly suppressed the first-phase insulin response. These data suggest that therapeutic levels of PIs are sufficient to impair glucose sensing by beta-cells. Thus, together with peripheral insulin resistance, beta-cell dysfunction likely contributes to altered glucose homeostasis associated with highly active antiretroviral therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Carr A, Samaras K, Burton S, Law M, Freund I, Chisholm DJ, Cooper DA. A syndrome of peripheral lipodystrophy, hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance in patients receiving HIV protease inhibitors. AIDS. 1998;12:F51–F58. - PubMed
-
- Vigouroux C, Gharakhanian S, Salhi Y, Nguyen TH, Chevenne D, Capeau J, Rozenbaum W. Diabetes, insulin resistance and dyslipidaemia in lipodystrophic HIV-infected patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) Diabetes Metab. 1999;25:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Hadigan C, Meigs JB, Corcoran C, Rietschel P, Piecuch S, Basgoz N, Davis B, Sax P, Stanley T, Wilson PW, D‘Agostino RB, Grinspoon S. Metabolic abnormalities and cardiovascular disease risk factors in adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection and lipodystrophy. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:130–139. - PubMed
-
- Murata H, Hruz PW, Mueckler M. The mechanism of insulin resistance caused by HIV protease inhibitor therapy. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:20251–20254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

