Mutations within the ADP (E3-11.6K) protein alter processing and localization of ADP and the kinetics of cell lysis of adenovirus-infected cells
- PMID: 12829816
- PMCID: PMC161948
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.14.7764-7778.2003
Mutations within the ADP (E3-11.6K) protein alter processing and localization of ADP and the kinetics of cell lysis of adenovirus-infected cells
Abstract
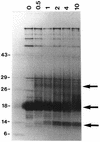
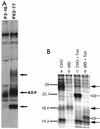
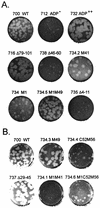
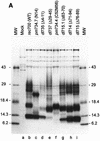
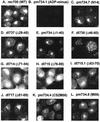
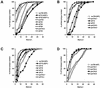
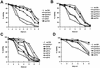
ADP (also known as E3-11.6K protein) is synthesized abundantly in late adenovirus infection and is required for efficient lysis of infected cells and release of viral progeny at the end of the viral replication cycle. ADP is a type III bitopic N(endo)C(exo) nuclear membrane and Golgi glycoprotein that is produced at high levels in late adenovirus infection (>24 h postinfection). We show pulse-chase and other studies indicating that ADP undergoes a complex process of N- and O-linked glycosylation and proteolytic cleavage. In order to further characterize ADP, a series of 23 deletion and point mutations has been constructed in the adenovirus serotype 2 adp gene and then built into a wild-type adenovirus background. These mutants were analyzed for processing and intracellular localization of ADP. Mutation of the single predicted N glycosylation site eliminated N glycosylation. Deletion of a region in ADP rich in serine and threonine residues reduced O glycosylation. In general, mutations within the lumenal domain of ADP resulted in lower protein stability; immunofluorescence assays indicated that these ADPs were primarily present in the Golgi apparatus. Viruses with mutations within the cytoplasmic-nucleoplasmic domain of ADP showed normal glycosylation patterns and protein abundance for ADP, but the protein was often found throughout cellular membranes rather than being localized specifically to the nuclear membrane and Golgi apparatus. The ADP virus mutants were analyzed by cell viability assays to determine the kinetics of cell lysis following infection of human A549 cells. In general, viruses with mutations within the lumenal domain of ADP display greatly reduced efficiencies of cell lysis. Viruses with large deletions in the cytoplasmic-nucleoplasmic domain of ADP retain much of their ability to lyse infected cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The adenovirus death protein (E3-11.6K) is required at very late stages of infection for efficient cell lysis and release of adenovirus from infected cells.J Virol. 1996 Apr;70(4):2296-306. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.4.2296-2306.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8642656 Free PMC article.
-
The E3-11.6-kDa adenovirus death protein (ADP) is required for efficient cell death: characterization of cells infected with adp mutants.Virology. 1996 Jun 1;220(1):152-62. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0295. Virology. 1996. PMID: 8659107
-
Adenovirus ADP protein (E3-11.6K), which is required for efficient cell lysis and virus release, interacts with human MAD2B.Virology. 2003 Aug 15;313(1):224-34. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00287-3. Virology. 2003. PMID: 12951035
-
The Adenovirus Death Protein - a small membrane protein controls cell lysis and disease.FEBS Lett. 2020 Jun;594(12):1861-1878. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13848. Epub 2020 Jun 19. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 32472693 Review.
-
Immunomodulatory functions encoded by the E3 transcription unit of adenoviruses.Virus Genes. 2000;21(1-2):13-25. Virus Genes. 2000. PMID: 11022786 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic identification of adenovirus type 5 genes that influence viral spread.J Virol. 2006 Feb;80(4):2000-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.4.2000-2012.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16439556 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a prototype immunochromatographic test for rapid diagnosis of respiratory adenovirus infection.Braz J Infect Dis. 2017 Sep-Oct;21(5):500-506. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2017.03.023. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Braz J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28623675 Free PMC article.
-
The FDA-Approved Drug Nelfinavir Inhibits Lytic Cell-Free but Not Cell-Associated Nonlytic Transmission of Human Adenovirus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Aug 20;64(9):e01002-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01002-20. Print 2020 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32601166 Free PMC article.
-
Verapamil enhances the antitumoral efficacy of oncolytic adenoviruses.Mol Ther. 2010 May;18(5):903-11. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.22. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Mol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20179683 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting host O-linked glycan biosynthesis affects Ebola virus replication efficiency and reveals differential GalNAc-T acceptor site preferences on the Ebola virus glycoprotein.J Virol. 2024 Jun 13;98(6):e0052424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00524-24. Epub 2024 May 17. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38757972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Doronin, K., K. Toth, M. Kuppuswamy, P. Krajcsi, A. E. Tollefson, and W. S. M. Wold. 2003. Overexpression of the ADP (E3-11.6K) protein increases cell lysis and spread of adenovirus. Virology 305:378-387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

