The importance of the nine-amino acid C-terminal sequence of exendin-4 for binding to the GLP-1 receptor and for biological activity
- PMID: 12832104
- PMCID: PMC10031803
- DOI: 10.1016/s0167-0115(03)00120-4
The importance of the nine-amino acid C-terminal sequence of exendin-4 for binding to the GLP-1 receptor and for biological activity
Abstract
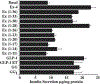
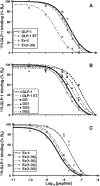
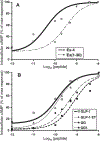
Exendin-4, a 39-amino acid (AA) peptide, is a long-acting agonist at the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor. Consequently, it may be preferable to GLP-1 as a long-term treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exendin-4 (Ex-4), unlike GLP-1, is not degraded by dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV), is less susceptible to degradation by neutral endopeptidase, and possesses a nine-AA C-terminal sequence absent from GLP-1. Here we examine the importance of these nine AAs for biological activity of Ex-4, a sequence of truncated Ex-4 analogs, and native GLP-1 and GLP-1 analogs to which all or parts of the C-terminal sequence have been added. We found that removing these AAs from Ex-4 to produce Ex (1-30) reduced the affinity for the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) relative to Ex-4 (IC50: Ex-4, 3.22+/-0.9 nM; Ex (1-30), 32+/-5.8 nM) but made it comparable to that of GLP-1 (IC50: 44.9+/-3.2 nM). The addition of this nine-AA sequence to GLP-1 improved the affinity of both GLP-1 and the DPP IV resistant analog GLP-1 8-glycine for the GLP-1 receptor (IC50: GLP-1 Gly8 [GG], 220+/-23 nM; GLP-1 Gly8 Ex (31-39), 74+/-11 nM). Observations of the cAMP response in an insulinoma cell line show a similar trend for biological activity.
Figures
References
-
- Nathan DM, Schreiber E, Fogel H, Mojsov S, Habener JF. Insulinotropic action of glucagonlike peptide-I-(7–37) in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 1992;15:270–6. - PubMed
-
- Zander M, Madsbad S, Madsen JL, Holst JJ. Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a parallel-group study. Lancet 2002;359:824–30. - PubMed
-
- Stoffers DA, Kieffer TJ, Hussain MA, Drucker DJ, Bonner-Weir S, Habener JF, et al. Insulinotropic glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists stimulate expression of homeodomain protein IDX-1 and increase islet size in mouse pancreas. Diabetes 2000;49:741–8. - PubMed
-
- Perfetti R, Zhou J, Doyle ME, Egan JM. Glucagon-like peptide-1 induces cell proliferation and pancreatic-duodenum homeobox-1 expression and increases endocrine cell mass in the pancreas of old, glucose-intolerant rats. Endocrinology 2000;141:4600–5. - PubMed
-
- Kieffer TJ, McIntosh CH, Pederson RA. Degradation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and truncated glucagon-like peptide 1 in vitro and in vivo by dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Endocrinology 1995;136:3585–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

