Targeted disruption of the mouse rho-associated kinase 2 gene results in intrauterine growth retardation and fetal death
- PMID: 12832488
- PMCID: PMC162229
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.14.5043-5055.2003
Targeted disruption of the mouse rho-associated kinase 2 gene results in intrauterine growth retardation and fetal death
Abstract
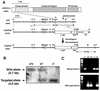
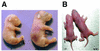
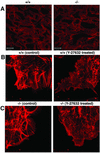
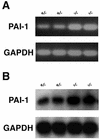
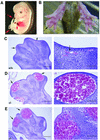
Rho-associated kinase (ROCK), including the ROCK-I and ROCK-II isoforms, is a protein kinase involved in signaling from Rho to actin cytoskeleton. However, in vivo functions of each ROCK isoform remain largely unknown. We generated mice deficient in ROCK-II by gene targeting. ROCK-II(-/-) embryos were found at the expected Mendelian frequency until 13.5 days postcoitum, but approximately 90% died thereafter in utero. ROCK-II(-/-) mice of both genders that survived were born runts, subsequently developed without gross abnormality, and were fertile. Whole-mount staining for a knocked-in lacZ reporter gene revealed that ROCK-II was highly expressed in the labyrinth layer of the placenta. Disruption of architecture and extensive thrombus formation were found in the labyrinth layer of ROCK-II(-/-) mice. While no obvious alteration in actin filament structures was found in the labyrinth layer of ROCK-II(-/-) placenta and stress fibers were formed in cultured ROCK-II(-/-) trophoblasts, elevated expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 was found in ROCK-II(-/-) placenta. These results suggest that ROCK-II is essential in inhibiting blood coagulation and maintaining blood flow in the endothelium-free labyrinth layer and that loss of ROCK-II leads to thrombus formation, placental dysfunction, intrauterine growth retardation, and fetal death.
Figures



References
-
- Adams, R. H., A. Porras, G. Alonso, M. Jones, K. Vintersten, S. Panelli, A. Valladeres, L. Perez, R. Klein, and N. R. Nebreda. 2000. Essential role of p38alpha MAP kinase in placenta but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol. Cell 6:109-116. - PubMed
-
- Adamson, S. L., Y. Lu, K. J. Whitley, D. Holmyard, M. Hemberger, C. Pfarrer, and J. C. Cross. 2002. Interaction between trophoblast cells and the maternal and fetal circulation in the mouse placenta. Dev. Biol. 250:358-373. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Sagi, D., and A. Hall. 2000. Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion. Cell 103:227-238. - PubMed
-
- Collen, D. 1999. The plasminogen (fibrinolytic) system. Thromb. Haemostasis 82:259-270. - PubMed
-
- Erickson, L. A., J. F. Gregory, J. E. Lund, T. P. Boyle, H. G. Polites, and K. R. Marotti. 1990. Development of venous occlusions in mice transgenic for the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene. Nature 346:74-76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
