Nongenomic glucocorticoid inhibition via endocannabinoid release in the hypothalamus: a fast feedback mechanism
- PMID: 12832507
- PMCID: PMC6741208
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-12-04850.2003
Nongenomic glucocorticoid inhibition via endocannabinoid release in the hypothalamus: a fast feedback mechanism
Abstract
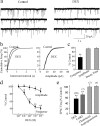
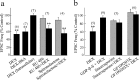
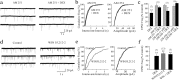
Glucocorticoid negative feedback in the brain controls stress, feeding, and neural-immune interactions by regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, but the mechanisms of inhibition of hypothalamic neurosecretory cells have never been elucidated. Using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in an acute hypothalamic slice preparation, we demonstrate a rapid suppression of excitatory glutamatergic synaptic inputs to parvocellular neurosecretory neurons of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) by the glucocorticoids dexamethasone and corticosterone. The effect was maintained with dexamethasone conjugated to bovine serum albumin and was not seen with direct intracellular glucocorticoid perfusion via the patch pipette, suggesting actions at a membrane receptor. The presynaptic inhibition of glutamate release by glucocorticoids was blocked by postsynaptic inhibition of G-protein activity with intracellular GDP-beta-S application, implicating a postsynaptic G-protein-coupled receptor and the release of a retrograde messenger. The glucocorticoid effect was not blocked by the nitric oxide synthesis antagonist N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride or by hemoglobin but was blocked completely by the CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonists AM251 [N-(piperidin-1-yl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide] and AM281 [1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-N-4-morpholinyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide] and mimicked and occluded by the cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 [(beta)-(+)-[2,3-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(4-morpholinylmethyl)pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazin-6-yl]-1-naphthalenylmethanone mesylate], indicating that it was mediated by retrograde endocannabinoid release. Several peptidergic subtypes of parvocellular neuron, identified by single-cell reverse transcripton-PCR analysis, were subject to rapid inhibitory glucocorticoid regulation, including corticotropin-releasing hormone-, thyrotropin-releasing hormone-, vasopressin-, and oxytocin-expressing neurons. Therefore, our findings reveal a mechanism of rapid glucocorticoid feedback inhibition of hypothalamic hormone secretion via endocannabinoid release in the PVN and provide a link between the actions of glucocorticoids and cannabinoids in the hypothalamus that regulate stress and energy homeostasis.
Figures
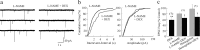
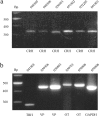
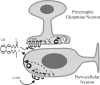
References
-
- Auclair N, Otani S, Soubrie P, Crepel F ( 2000) Cannabinoids modulate synaptic strength and plasticity at glutamatergic synapses of rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 83: 3287–3293. - PubMed
-
- Avanzino GL, Ermirio R, Ruggeri P, Cogo CE ( 1987) Effects of corticosterone on neurons of reticular formation in rats. Am J Physiol 253: R25–R30. - PubMed
-
- Bredt DS, Hwang PM, Snyder SH ( 1990) Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature 347: 768–770. - PubMed
-
- Burlet AJ, Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Chapleur-Chateau M, Burlet CR, Leibowitz SF ( 1992) Effect of food deprivation and refeeding on the concentration of vasopressin and oxytocin in discrete hypothalamic sites. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43: 897–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
