Characterization and epitope mapping of human monoclonal antibodies to PDC-E2, the immunodominant autoantigen of primary biliary cirrhosis
- PMID: 1283300
- PMCID: PMC2965520
- DOI: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90187-u
Characterization and epitope mapping of human monoclonal antibodies to PDC-E2, the immunodominant autoantigen of primary biliary cirrhosis
Abstract
Further to define the epitopes of PDC-E2, the major autoantigen in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), we have developed and characterized five human monoclonal antibodies. These antibodies were derived by fusing a regional hepatic lymph node from a patient with PBC with the mouse human heterohybrid cell line F3B6. Previous studies of epitope mapping of PDC-E2 have relied on whole sera and have suggested that the immunodominant epitope lies within the inner lipoyl domain of the molecule. However, selective absorption studies using whole sera and a series of overlapping recombinant peptides of PDC-E2 have suggested that the epitope may also include a large conformational component. Moreover, several laboratories have suggested that autoantibodies against the 2-oxo acids dehydrogenase autoantigens are cross-reactive. The five monoclonal antibodies generated included three IgG2a and two IgM antibodies and were studied for antigen specificity using recombinant PDC-E2, recombinant BCKD-E2, histone, dsDNA, IgG (Fc), collagen and a recombinant irrelevant liver specific control, the F alloantigen. The antibodies were also used to probe blots of human, bovine, mouse and rat mitochondria. Finally, fine specificity was studied by selective ELISA and absorption against overlapping expressing fragments of PDC-E2. All five monoclonals, but none of the other mitochondrial autoantigens were specific for PDC-E2. In fact, although affinity purified antibodies to PDC-E2 from patients with PBC cross-reacted with protein X, the human monoclonals did not, suggesting that protein X contains an epitope distinct from that found on PDC-E2. Additionally, all three IgG2 monoclonals recognized distinct epitopes within the inner lipoyl domain of PDC-E2.
Figures

 ds DNA; ▧ IgG (Fc); □ collagen; ▩ F protein; ▤ rBCKD-E2
ds DNA; ▧ IgG (Fc); □ collagen; ▩ F protein; ▤ rBCKD-E2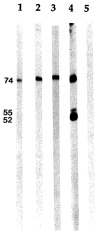


References
-
- Kaplan MM. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Adv Intern Med. 1987;32:359–377. - PubMed
-
- Gershwin ME, I, Mackay R. Primary biliary cirrhosis: paradigm or paradox for autoimmunity. Gastroenterol. 1991;100:822–833. - PubMed
-
- Van de Water J, Surh CD, Leung PS, Krams SM, Fregeau D, Davis P, Coppel R, Mackay IR, Gershwin ME. Molecular definitions, autoepitopes, and enzymatic activities of the mitochondrial autoantigens of primary biliary cirrhosis. Sem Liv Dis. 1989;9:132–137. - PubMed
-
- Mackay IR, Gershwin ME. Primary biliary cirrhosis: considerations on pathogenesis based on identification of the M2 autoantigens. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1990;12:101–119. - PubMed
-
- Bassendine MF, Fussey SP, Mutimer DJ, James OF, Yeaman SJ. Identification and characterization of four M2 mitochondrial autoantigens in primary biliary cirrhosis. Semn Liv Dis. 1989;9:124–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
