Coordinate repression of regulators of embryonic identity by PICKLE during germination in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12834400
- PMCID: PMC2515612
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01783.x
Coordinate repression of regulators of embryonic identity by PICKLE during germination in Arabidopsis
Abstract
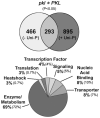
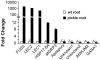
In angiosperms, germination represents an important developmental transition during which embryonic identity is repressed and vegetative identity emerges. PICKLE (PKL) encodes a CHD3-chromatin-remodeling factor necessary for the repression of expression of LEAFY COTYLEDON1 (LEC1), a central regulator of embryogenesis. A candidate gene approach and microarray analysis identified nine additional genes that exhibit PKL-dependent repression of expression during germination. Transcripts for all three LEAFY COTYLEDON genes, LEC1, LEC2, and FUS3, exhibit PKL-dependent repression, and all three transcripts are elevated more than 100-fold in pkl primary roots that inappropriately express embryonic traits (pickle roots). Three other genes that exhibit PKL-dependent regulation have expression patterns correlated with zygotic or somatic embryogenesis, and one gene encodes a putative Lin-11, Isl-1, MEC-3 (LIM) domain transcriptional regulator that is preferentially expressed in siliques. Genes that exhibit PKL-dependent repression during germination are not necessarily regulated by PKL at other points in development. Our data suggest that PKL selectively regulates a suite of genes during germination to repress embryonic identity. In particular, we propose that PKL acts as a master regulator of the LEAFY COTYLEDON genes, and that joint derepression of these genes is likely to contribute substantially to expression of embryonic identity in pkl seedlings.
Figures


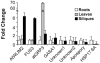
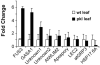
Similar articles
-
The CHD3 remodeler PICKLE associates with genes enriched for trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27.Plant Physiol. 2012 May;159(1):418-32. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.194878. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22452853 Free PMC article.
-
PICKLE acts during germination to repress expression of embryonic traits.Plant J. 2005 Dec;44(6):1010-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02602.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 16359393 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of the LEAFY COTYLEDON 1/B3 regulatory network in plant embryo development by VP1/ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 3-LIKE B3 genes.Plant Physiol. 2007 Feb;143(2):902-11. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.092320. Epub 2006 Dec 8. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17158584 Free PMC article.
-
LEAFY COTYLEDON 2: A Regulatory Factor of Plant Growth and Seed Development.Genes (Basel). 2021 Nov 26;12(12):1896. doi: 10.3390/genes12121896. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional symmetry of the B3 network controlling seed development.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2008 Oct;11(5):548-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2008.06.015. Epub 2008 Aug 6. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2008. PMID: 18691932 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic activity during early plant embryogenesis.Biochem J. 2020 Oct 16;477(19):3743-3767. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190161. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 33045058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis seed germination responses to osmotic stress involve the chromatin modifier PICKLE.Plant Signal Behav. 2008 Jul;3(7):478-9. doi: 10.4161/psb.3.7.5679. Plant Signal Behav. 2008. PMID: 19704491 Free PMC article.
-
Embryogenic potential and expression of embryogenesis-related genes in conifers are affected by treatment with a histone deacetylase inhibitor.Planta. 2011 Sep;234(3):527-39. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1418-8. Epub 2011 May 4. Planta. 2011. PMID: 21541665 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis Histone Methyltransferase SUVH5 Is a Positive Regulator of Light-Mediated Seed Germination.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jun 27;10:841. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00841. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31316539 Free PMC article.
-
The turnip mutant of Arabidopsis reveals that LEAFY COTYLEDON1 expression mediates the effects of auxin and sugars to promote embryonic cell identity.Plant Physiol. 2006 Oct;142(2):526-41. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.080895. Epub 2006 Aug 25. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16935993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahringer J. NuRD and SIN3 histone deacetylase complexes in development. Trends Genet. 2000;16:351–356. - PubMed
-
- Dawid IB, Breen JJ, Toyama R. LIM domains: multiple roles as adapters and functional modifiers in protein interactions. Trends Genet. 1998;14:156–162. - PubMed
-
- Eliasson A, Gass N, Mundel C, Baltz R, Krauter R, Evrard JL, Steinmetz A. Molecular and expression analysis of a LIM protein gene family from flowering plants. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000;264:257–267. - PubMed
-
- Eshed Y, Baum SF, Bowman JL. Distinct mechanisms promote polarity establishment in carpels of Arabidopsis. Cell. 1999;99:199–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

