Crystal structure of the SarS protein from Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 12837797
- PMCID: PMC164878
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.14.4219-4225.2003
Crystal structure of the SarS protein from Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
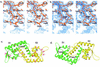
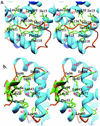
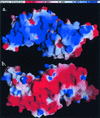
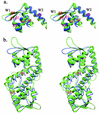
The expression of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus is controlled by global regulatory loci (e.g., sarA and agr). One of these determinants, protein A (spa), is activated by sarS, which encodes a 250-residue DNA-binding protein. Genetic analysis indicated that the agr locus likely mediates spa repression by suppressing the transcription of sarS. Contrary to SarA and SarR, which require homodimer formation for proper function, SarS is unusual within the SarA protein family in that it contains two homologous halves, with each half sharing sequence similarity to SarA and SarR. Here we report the 2.2 A resolution X-ray crystal structure of the SarS protein. SarS has folds similar to those of SarR and, quite plausibly, the native SarA structure. Two typical winged-helix DNA-binding domains are connected by a well-ordered loop. The interactions between the two domains are extensive and conserved. The putative DNA-binding surface is highly positively charged. In contrast, negatively charged patches are located opposite to the DNA-binding surface. Furthermore, sequence alignment and structural comparison revealed that MarR has folds similar to those of SarR and SarS. Members of the MarR protein family have previously been implicated in the negative regulation of an efflux pump involved in multiple antibiotic resistance in many gram-negative species. We propose that MarR also belongs to the winged-helix protein family and has a similar mode of DNA binding as SarR and SarS and possibly the entire SarA protein family member. Based on the structural differences of SarR, SarS, and MarR, we further classified these winged-helix proteins to three subfamilies, SarA, SarS, and MarR. Finally, a possible transcription regulation mechanism is proposed.
Figures

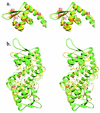
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the SarR protein from Staphylococcus aureus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 5;98(12):6877-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121013398. Epub 2001 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11381122 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the agr locus and the identification of DNA binding residues of the global regulatory protein SarR in Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Jun;60(5):1289-301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05171.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16689803
-
The SarA protein family of Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(3):355-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.10.032. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18083623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystal structures of SarA, a pleiotropic regulator of virulence genes in S. aureus.Nature. 2001 Jan 11;409(6817):215-9. doi: 10.1038/35051623. Nature. 2001. PMID: 11196648
-
Global regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus by the SarA protein family.Front Biosci. 2002 Aug 1;7:d1825-42. doi: 10.2741/A882. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 12133812 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and function analyses of the global regulatory protein SarA from Staphylococcus aureus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 14;103(7):2392-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510439103. Epub 2006 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16455801 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallographic studies of SarV, a global regulator from Staphylococcus aureus.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015 Aug;71(Pt 8):1038-41. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X15011097. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015. PMID: 26249696 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic regulation of the intercellular adhesion locus in staphylococci.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Mar 26;2:38. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00038. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23061050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attenuating Staphylococcus aureus virulence gene regulation: a medicinal chemistry perspective.J Med Chem. 2013 Feb 28;56(4):1389-404. doi: 10.1021/jm3014635. Epub 2013 Jan 22. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23294220 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory elements of the Staphylococcus aureus protein A (Spa) promoter.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(12):3738-48. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3738-3748.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15175287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alekshun, M. N., S. B. Levy, T. R. Mealy, B. A. Seaton, and J. F. Head. 2001. The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2.3 Å resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8:710-714. - PubMed
-
- Arvidson, S., and K. Tegmark. 2001. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 291:159-170. - PubMed
-
- Boyce, J. M. 1997. Epidemiology and prevention of nosocomial infections, p. 309-329. In K. B. Crossley and G. L. Archer (ed.), The staphylococci in human disease. Churchill Livingstone, New York, N.Y.
-
- Brunger, A. T., P. D. Adams, G. M. Clore, W. L. DeLano, P. Gros, R. W. Grosse-Kunstleve, J. S. Jiang, J. Kuszewski, M. Nilges, N. S. Pannu, R. J. Read, L. M. Rice, T. Simonson, and G. L. Warren. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54:905-921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

