Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the complete MADS-box transcription factor family in Arabidopsis: new openings to the MADS world
- PMID: 12837945
- PMCID: PMC165399
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.011544
Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the complete MADS-box transcription factor family in Arabidopsis: new openings to the MADS world
Abstract
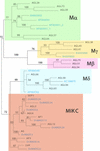
MADS-box transcription factors are key regulators of several plant development processes. Analysis of the complete Arabidopsis genome sequence revealed 107 genes encoding MADS-box proteins, of which 84% are of unknown function. Here, we provide a complete overview of this family, describing the gene structure, gene expression, genome localization, protein motif organization, and phylogenetic relationship of each member. We have divided this transcription factor family into five groups (named MIKC, Malpha, Mbeta, Mgamma, and Mdelta) based on the phylogenetic relationships of the conserved MADS-box domain. This study provides a solid base for functional genomics studies into this important family of plant regulatory genes, including the poorly characterized group of M-type MADS-box proteins. MADS-box genes also constitute an excellent system with which to study the evolution of complex gene families in higher plants.
Figures








References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla, E.R., Pelaz, S., Liljegren, S.J., Gold, S.E., Burgeff, C., Ditta, G.S., De Pouplana, L.R., Martínez-Castilla, L., and Yanofsky, M.F. (2000). An ancestral MADS-box gene duplication occurred before the divergence of plants and animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 5328–5333. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408, 796–815. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, T.L., and Elkan, C. (1994). Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. In Proceeding of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. (Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press), pp. 28–36. - PubMed
-
- Bowman, J.L., Alvarez, J., Weigel, D., Meyerowitz, E.M., and Smyth, D.R. (1993). Control of flower development in Arabidopsis thaliana by APETALA1 and interacting genes. Development 119, 721–743.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

