Changes in functional and histological distributions of nitric oxide synthase caused by chronic hypoxia in rat small pulmonary arteries
- PMID: 12839863
- PMCID: PMC1573911
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705312
Changes in functional and histological distributions of nitric oxide synthase caused by chronic hypoxia in rat small pulmonary arteries
Abstract
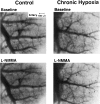
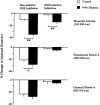
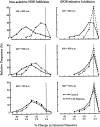
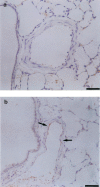
1. Chronic hypoxia (CH) increases lung tissue expression of all types of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in the rat. However, it remains unknown whether CH-induced changes in functional and histological NOS distributions are correlated in rat small pulmonary arteries. 2. We measured the effects of NOS inhibitors on the internal diameters (ID) of muscular (MPA) and elastic (EPA) pulmonary arteries (100-700 micro m ID) using an X-ray television system on anaesthetized rats. We also conducted NOS immunohistochemical localization on the same vessels. 3. Nonselective NOS inhibitors induced ID reductions in almost all MPA of CH rats (mean reduction, 36+/-3%), as compared to approximately 60% of control rat MPA (mean, 10+/-2%). The inhibitors reduced the ID of almost all EPA with similar mean values (approximately 26%) in both CH and control rats. On the other hand, inducible NOS (iNOS)-selective inhibitors caused ID reductions in approximately 60% of CH rat MPA (mean, 15+/-3%), but did so in only approximately 20% of control rat MPA (mean, 2+/-2%). This inhibition caused only a small reduction (mean, approximately 4%) in both CH and control rat EPA. A neuronal NOS-selective inhibitor had no effect. 4. The percentage of endothelial NOS (eNOS)-positive vessels was approximately 96% in both MPA and EPA from CH rats, whereas it was 51 and 91% in control MPA and EPA, respectively. The percentage for iNOS was approximately 60% in both MPA and EPA from CH rats, but was only approximately 8% in both arteries from control rats. 5. The data indicate that in CH rats, both functional and histological upregulation of eNOS extensively occurs within MPA. iNOS protein increases sporadically among parallel-arranged branches in both MPA and EPA, but its vasodilatory effect is predominantly observed in MPA. Such NOS upregulation may serve to attenuate hypoxic vasoconstriction, which occurs primarily in MPA and inhibit the progress of pulmonary hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- ABRAHAM A.S., KAY J.M., COLE R.B., PINCOCK A.C. Haemodynamic and pathological study of the effect of chronic hypoxia and subsequent recovery of the heart and pulmonary vasculature of the rat. Cardiovasc. Res. 1971;5:95–102. - PubMed
-
- ALBERTINI M., VANELLI G., CLEMENT G. PGI2 and nitric oxide involvement in the regulation of systemic and pulmonary basal vascular tone in the pig. Prostaglandins Leukotr. Essent. Fatty Acids. 1996;54:273–278. - PubMed
-
- BARNARD J.W., WILSON P.S., MOORE T.M., THOMPSON W.J., TAYLOR A.E. Effect of nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase products on vascular resistance in dog and rat lungs. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993;74:2940–2948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

