Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated JNK activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells by pharmacological and adenovirus-mediated inhibition of inhibitory kappa B kinase signalling
- PMID: 12839879
- PMCID: PMC1573924
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705330
Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated JNK activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells by pharmacological and adenovirus-mediated inhibition of inhibitory kappa B kinase signalling
Abstract
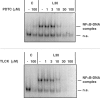
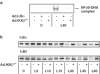
1. In rat aortic smooth muscle cells (RASMCs), the putative nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) inhibitor Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) was found to inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated NFkappaB DNA-binding. However, further investigation identified the site of inhibition as being at, or upstream of, the inhibitory kappa B kinases (IKKs) as their kinase activity was substantially reduced. 2. In addition, PDTC potentiated LPS-stimulated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase) and MAP kinase-activated protein kinase-2 activity (the downstream target of p38 MAP kinase). 3. Another inhibitor of NFkappaB signalling, the serine protease inhibitor Nalphap-tosyl-L-lysine chloro-methylketone (TLCK), also inhibited LPS-stimulated IKK activity and potentiated JNK activity in response to LPS, suggesting that cross-talk may occur between the NFkappaB and stress-activated protein kinase pathways at the level of IKK or at a common point upstream. 4. Infection of RASMCs with an adenovirus encoding either inhibitory kappa Balpha or a dominant-negative IKKbeta potentiated LPS-stimulated JNK activity. 5. These studies therefore suggest that the loss of NFkappaB DNA-binding and resultant transcriptional activity, rather than the loss of IKK activity, is sufficient to cause an increase in JNK activity. This shows that either pharmacological or molecular inhibition of NFkappaB DNA-binding enhances JNK activation in vascular smooth muscle cells, an effect that may contribute to the pathophysiological effects of LPS.
Figures





References
-
- BOWIE A.G., MOYNAGH P.N., O'NEILL L.A.J. Lipid peroxidation is involved in the activation of NF-kappaB by tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-1 in the human endothelial cell line ECV304. Lack of involvement of H2O2 in NF-kappaB activation by either cytokine in both primary and transformed endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:25941–25950. - PubMed
-
- BOWIE A.G., O'NEILL L.A. Vitamin C inhibits NF-kappa B activation by TNF via the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Immunol. 2000;165:7180–7188. - PubMed
-
- BRENNAN P., O'NEILL L.A.J. 2-mercaptoethanol restores the ability of nuclear factor kappa B (NF kappa B) to bind DNA in nuclear extracts from interleukin 1-treated cells incubated with pyrollidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC). Evidence for oxidation of glutathione in the mechanism of inhibition of NF kappa B by PDTC. Biochem. J. 1996;320:975–981. - PMC - PubMed
-
- CHAE H., CHAE S., PARK N., BANG B., CHO S., KIM J., KIM H., LEE Z. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits serum-induced NF-kappaB activation and induces apoptosis in ROS 17/2.8 osteoblasts. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001;1:255–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

