Structural basis of the interaction between RalA and Sec5, a subunit of the sec6/8 complex
- PMID: 12839989
- PMCID: PMC165653
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg329
Structural basis of the interaction between RalA and Sec5, a subunit of the sec6/8 complex
Abstract
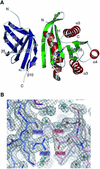
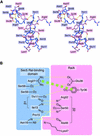
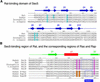
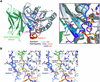
The sec6/8 complex or exocyst is an octameric protein complex that functions during cell polarization by regulating the site of exocytic vesicle docking to the plasma membrane, in concert with small GTP-binding proteins. The Sec5 subunit of the mammalian sec6/8 complex binds Ral in a GTP-dependent manner. Here we report the crystal structure of the complex between the Ral-binding domain of Sec5 and RalA bound to a non-hydrolyzable GTP analog (GppNHp) at 2.1 A resolution, providing the first structural insights into the mechanism and specificity of sec6/8 regulation. The Sec5 Ral-binding domain folds into an immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich structure, which represents a novel fold for an effector of a GTP-binding protein. The interface between the two proteins involves a continuous antiparallel beta-sheet, similar to that found in other effector/G-protein complexes, such as Ras and Rap1A. Specific interactions unique to the RalA.Sec5 complex include Sec5 Thr11 and Arg27, and RalA Glu38, which we show are required for complex formation by isothermal titration calorimetry. Comparison of the structures of GppNHp- and GDP-bound RalA suggests a nucleotide-dependent switch mechanism for Sec5 binding.
Figures
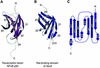


References
-
- Abrahams J.P. and Leslie,A.G.W. (1996) Methods used in the structure determination of bovine mitochondrial F1 ATPase. Acta Crystallogr. D, 52, 30–42. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S.F., Gish,W., Miller,W., Myers,E.W. and Lipman,D.J. (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol., 215, 403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

