MEKK1 regulates calpain-dependent proteolysis of focal adhesion proteins for rear-end detachment of migrating fibroblasts
- PMID: 12839996
- PMCID: PMC165646
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg322
MEKK1 regulates calpain-dependent proteolysis of focal adhesion proteins for rear-end detachment of migrating fibroblasts
Abstract
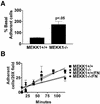
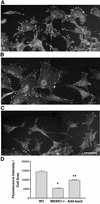
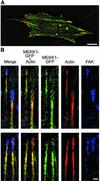
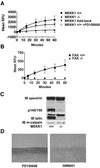
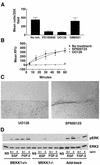
Herein, we define how MEKK1, a MAPK kinase kinase, regulates cell migration. MEKK1 is associated with actin fibers and focal adhesions, localizing MEKK1 to sites critical in the control of cell adhesion and migration. EGF-induced ERK1/2 activation and chemotaxis are inhibited in MEKK1-/- fibroblasts. MEKK1 deficiency causes loss of vinculin in focal adhesions of migrating cells, increased cell adhesion and impeded rear-end detachment. MEKK1 is required for activation of the cysteine protease calpain and cleavage of spectrin and talin, proteins linking focal adhesions to the cytoskeleton. Inhibition of ERK1/2 or calpain, but not of JNK, mimics MEKK1 deficiency. Therefore, MEKK1 regulates calpain-mediated substratum release of migrating fibroblasts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MEK kinase 1 interacts with focal adhesion kinase and regulates insulin receptor substrate-1 expression.J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 7;278(6):3846-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206087200. Epub 2002 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12458213
-
Reduced cell migration and disruption of the actin cytoskeleton in calpain-deficient embryonic fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 21;276(51):48382-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108893200. Epub 2001 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11602605
-
Interferon-inducible protein 9 (CXCL11)-induced cell motility in keratinocytes requires calcium flux-dependent activation of mu-calpain.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(5):1922-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.5.1922-1941.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15713646 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the three dimensional architecture of focal adhesion components to explain Ca2+-mediated turnover of focal adhesions.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Mar;1861(3):624-635. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28063985
-
The calpain system and cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2011 May;11(5):364-74. doi: 10.1038/nrc3050. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21508973 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurodevelopmental disorders, immunity, and cancer are connected.iScience. 2022 May 30;25(6):104492. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104492. eCollection 2022 Jun 17. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35712080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEKK2 regulates paxillin ubiquitylation and localization in MDA-MB 231 breast cancer cells.Biochem J. 2014 Nov 15;464(1):99-108. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140420. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25190348 Free PMC article.
-
ERK-ERF-EGR1, a novel switch underlying acquisition of a motile phenotype.Cell Adh Migr. 2013 Jan-Feb;7(1):33-7. doi: 10.4161/cam.22263. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2013. PMID: 23076209 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain activity is essential in skin wound healing and contributes to scar formation.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037084. Epub 2012 May 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615899 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-actinin 4 and tumorigenesis of breast cancer.Vitam Horm. 2013;93:323-51. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416673-8.00005-8. Vitam Horm. 2013. PMID: 23810014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beckerle M.C., Burridge,K., DeMartino,G.N. and Croall,D.E. (1987) Colocalization of calcium-dependent protease II and one of its substrates at sites of cell adhesion. Cell, 51, 569–577. - PubMed
-
- Bialkowska K., Kulkarni,S., Du,X., Goll,D.E., Saido,T.C. and Fox,J.E. (2000) Evidence that β3 integrin-induced Rac activation involves the calpain-dependent formation of integrin clusters that are distinct from the focal complexes and focal adhesions that form as Rac and RhoA become active. J. Cell Biol., 151, 685–696. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christerson L.B., Vanderbilt,C.A. and Cobb,M.H. (1999) MEKK1 interacts with α-actinin and localizes to stress fibers and focal adhesions. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton, 43, 186–198. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

