The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2
- PMID: 12840003
- PMCID: PMC165640
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg315
The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2
Abstract
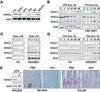
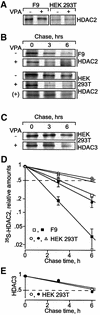
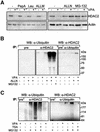
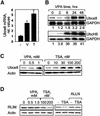
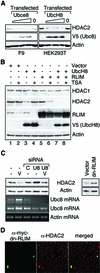
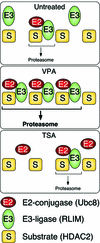
Histone-modifying enzymes play essential roles in physiological and aberrant gene regulation. Since histone deacetylases (HDACs) are promising targets of cancer therapy, it is important to understand the mechanisms of HDAC regulation. Selective modulators of HDAC isoenzymes could serve as efficient and well-tolerated drugs. We show that HDAC2 undergoes basal turnover by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Valproic acid (VPA), in addition to selectively inhibiting the catalytic activity of class I HDACs, induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2, in contrast to other inhibitors such as trichostatin A (TSA). Basal and VPA-induced HDAC2 turnover critically depend on the E2 ubiquitin conjugase Ubc8 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase RLIM. Ubc8 gene expression is induced by both VPA and TSA, whereas only TSA simultaneously reduces RLIM protein levels and therefore fails to induce HDAC2 degradation. Thus, poly-ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation provide an isoenzyme-selective mechanism for downregulation of HDAC2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Valproic acid: an old drug newly discovered as inhibitor of histone deacetylases.Ann Hematol. 2004;83 Suppl 1:S91-2. doi: 10.1007/s00277-004-0850-2. Ann Hematol. 2004. PMID: 15124690 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce apoptosis, histone hyperacetylation and up-regulation of gene transcription in Schistosoma mansoni.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2009 Nov;168(1):7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2009.06.001. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19538992
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitors suberoylanilide hydroxamic (Vorinostat) and valproic acid induce irreversible and MDR1-independent resistance in human colon cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2007 Sep;31(3):633-41. Int J Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17671692
-
Modulation of angiogenesis-related protein synthesis by valproic acid.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Apr 9;316(3):693-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.02.105. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15033455
-
The Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway and Epigenetic Modifications in Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(1):20-32. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200811114159. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32781973 Review.
Cited by
-
Brief review on repurposed drugs and vaccines for possible treatment of COVID-19.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 May 5;898:173977. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173977. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33639193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone/protein deacetylases and T-cell immune responses.Blood. 2012 Mar 15;119(11):2443-51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-292003. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22246031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potentiation of the anticancer effect of valproic acid, an antiepileptic agent with histone deacetylase inhibitory activity, by the kinase inhibitor Staurosporine or its clinically relevant analogue UCN-01.Br J Cancer. 2006 May 22;94(10):1436-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603132. Br J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16705314 Free PMC article.
-
Valproic acid affects membrane trafficking and cell-wall integrity in fission yeast.Genetics. 2007 Apr;175(4):1695-705. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.070946. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17287531 Free PMC article.
-
Valproic acid as a radio-sensitizer in glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurooncol Pract. 2022 Sep 30;10(1):13-23. doi: 10.1093/nop/npac078. eCollection 2023 Feb. Neurooncol Pract. 2022. PMID: 36659976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alland L., Muhle,R., Hou,H.,Jr, Potes,J., Chin,L., Schreiber-Agus,N. and DePinho,R.A. (1997) Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature, 387, 49–55. - PubMed
-
- Bach I. et al. (1999) RLIM inhibits functional activity of LIM homeodomain transcription factors via recruitment of the histone deacetylase complex. Nat. Genet., 22, 394–399. - PubMed
-
- Carrano A.C., Eytan,E., Hershko,A. and Pagano,M. (1999) SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 193–199. - PubMed
-
- David G., Neptune,M.A. and DePinho,R.A. (2002) SUMO-1 modification of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) modulates its biological activities. J. Biol. Chem., 277, 23658–23663. - PubMed
-
- Driever P.H., Knüpfer,M.M., Cinatl,J. and Wolff,J.E. (1999) Valproic acid for the treatment of pediatric malignant glioma. Klin. Pädiatr., 211, 323–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

