CRN-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans FEN-1 homologue, cooperates with CPS-6/EndoG to promote apoptotic DNA degradation
- PMID: 12840007
- PMCID: PMC165645
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg320
CRN-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans FEN-1 homologue, cooperates with CPS-6/EndoG to promote apoptotic DNA degradation
Abstract
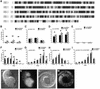
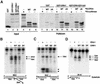
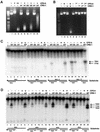
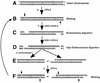
Oligonucleosomal fragmentation of chromosomes in dying cells is a hallmark of apoptosis. Little is known about how it is executed or what cellular components are involved. We show that crn-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans homologue of human flap endonuclease-1 (FEN-1) that is normally involved in DNA replication and repair, is also important for apoptosis. Reduction of crn-1 activity by RNA interference resulted in cell death phenotypes similar to those displayed by a mutant lacking the mitochondrial endonuclease CPS-6/endonuclease G. CRN-1 localizes to nuclei and can associate and cooperate with CPS-6 to promote stepwise DNA fragmentation, utilizing the endonuclease activity of CPS-6 and both the 5'-3' exonuclease activity and a previously uncharacterized gap-dependent endonuclease activity of CRN-1. Our results suggest that CRN-1/FEN-1 may play a critical role in switching the state of cells from DNA replication/repair to DNA degradation during apoptosis.
Figures
References
-
- Bambara R.A., Murante,R.S. and Henricksen,L.A. (1997) Enzymes and reactions at the eukaryotic DNA replication fork. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 4647–4650. - PubMed
-
- Enari M., Sakahira,H., Yokoyama,H., Okawa,K., Iwamatsu,A. and Nagata,S. (1998) A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature, 391, 43–50. - PubMed
-
- Horvitz H.R. (1999) Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Cancer Res., 59, 1701s–1706s. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

