High-neurovirulence GDVII virus induces apoptosis in murine astrocytes through tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-receptor and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- PMID: 12842625
- PMCID: PMC7127641
- DOI: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00157-0
High-neurovirulence GDVII virus induces apoptosis in murine astrocytes through tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-receptor and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
Abstract
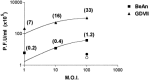
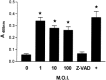
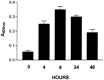
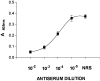
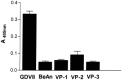
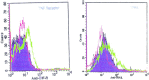
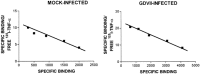
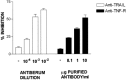
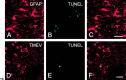
We carried out a study to determine if the high-neurovirulence GDVII strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) and the demyelinating, low-neurovirulence BeAn strain induced apoptosis in murine astrocytes. Astrocytes, the major glial cell population of the central nervous system, were semipermissive for GDVII virus replication. Programmed cell death, demonstrated by apoptosis-specific caspase-3 protease activity, was maximal 8 h after GDVII infection at an m.o.i. of 1. Purified TMEV capsid proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 did not induce apoptosis but antibodies to VP1 and VP2 inhibited it. Antibody inhibition of caspase-3 activity as well as flow cytometry experiments implicated TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and TNF-alpha-receptor (TNF-R) in apoptosis signaling. Conversely, TNF-alpha and the TRAIL-receptor were not upregulated. Furthermore, the number of functional TNF-alpha receptors, but not their affinity, was increased in apoptotic GDVII virus-infected astrocytes, as confirmed in binding experiments with 125I-labeled recombinant murine TNF-alpha. In vivo studies showed that most of the cells loaded with the virus when injected in the brains of SJL mice were neurons but very few showed TUNEL costaining. Conversely, many of the apoptotic cells found were also positive for GFAP staining.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus induces apoptosis in gamma interferon-activated M1 differentiated myelomonocytic cells through a mechanism involving tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and TNF-alpha-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.J Virol. 2001 Jul;75(13):5930-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.13.5930-5938.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11390594 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) VP1 carboxyl region on the virus-induced central nervous system disease.J Neurovirol. 1995 Mar;1(1):101-10. doi: 10.3109/13550289509111014. J Neurovirol. 1995. PMID: 9222346
-
The neurovirulence of the DA and GDVII strains of Theiler's virus correlates with their ability To infect cultured neurons.J Virol. 1998 Sep;72(9):7213-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7213-7220.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9696815 Free PMC article.
-
Differential usage of carbohydrate co-receptors influences cellular tropism of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus infection of the central nervous system.Glycoconj J. 2006 Feb;23(1-2):39-49. doi: 10.1007/s10719-006-5436-x. Glycoconj J. 2006. PMID: 16575521 Review.
-
Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV): the role of a small out-of-frame protein in viral persistence and demyelination.Jpn J Infect Dis. 1999 Dec;52(6):228-33. Jpn J Infect Dis. 1999. PMID: 10738359 Review.
Cited by
-
An in vitro experimental model of neuroinflammation: the induction of interleukin-6 in murine astrocytes infected with Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus, and its inhibition by oestrogenic receptor modulators.Immunology. 2011 Jul;133(3):360-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03448.x. Epub 2011 May 13. Immunology. 2011. PMID: 21564094 Free PMC article.
-
Theiler's virus infection provokes the overexpression of genes coding for the chemokine Ip10 (CXCL10) in SJL/J murine astrocytes, which can be inhibited by modulators of estrogen receptors.J Neurovirol. 2014 Oct;20(5):485-95. doi: 10.1007/s13365-014-0273-3. Epub 2014 Jul 23. J Neurovirol. 2014. PMID: 25052192
-
Overexpression of caspase 1 in apoptosis-resistant astrocytes infected with the BeAn Theiler's virus.J Neurovirol. 2016 Jun;22(3):316-26. doi: 10.1007/s13365-015-0400-9. Epub 2015 Nov 13. J Neurovirol. 2016. PMID: 26567013
-
Survivin prevents apoptosis by binding to caspase-3 in astrocytes infected with the BeAn strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus.J Neurovirol. 2012 Oct;18(5):354-63. doi: 10.1007/s13365-012-0112-3. Epub 2012 May 26. J Neurovirol. 2012. PMID: 22638909
-
Mechanisms of reovirus-induced cell death and tissue injury: role of apoptosis and virus-induced perturbation of host-cell signaling and transcription factor activation.Viral Immunol. 2005;18(1):89-115. doi: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.89. Viral Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15802955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allsopp T.E., Fazakerley J.K. Altruistic cell suicide and the specialized case of the virus-infected nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:284–290. - PubMed
-
- Alnemri E.S., Livingston D.J., Nicholson D.W., Salvesen G., Thornberry N.A., Wong W.W., Yuan J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell. 1996;87:171. - PubMed
-
- Aranguez E., Torres C., Rubio N. The receptor for tumor necrosis factor on murine astrocytes: characterization, intracellular degradation, and regulation by cytokines and Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus. Glia. 1995;13:185–194. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

