High prevalence of M184 mutation among patients with viroimmunologic discordant responses to highly active antiretroviral therapy and outcomes after change of therapy guided by genotypic analysis
- PMID: 12843034
- PMCID: PMC165358
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.7.3007-3012.2003
High prevalence of M184 mutation among patients with viroimmunologic discordant responses to highly active antiretroviral therapy and outcomes after change of therapy guided by genotypic analysis
Abstract
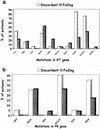
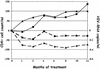
Whether highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) should be modified in patients with persistent increases in CD4(+) T cells despite detectable viral loads is an unresolved question. Forty-three heavily pretreated human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients with virologic failure during HAART were studied before a change of therapy guided by genotypic analysis and during follow-up. Patients with an increase in CD4(+) cell count (>100 cells/ml) over pre-HAART values were considered to be discordant patients (20 individuals), whereas patients with a lower increase or no increase in CD4(+) cell count were considered failing patients (23 individuals). Based on univariate analysis, a high CD4(+) cell count before antiretroviral treatment, homosexual behavior as a risk factor for HIV infection, reduced drug exposure to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, low replicative capacity of HIV isolates, and more frequent detection of HIV isolates with a non-B subtype, an R5 biological phenotype, and M184V and T215Y/F mutations were factors associated with a discordant response to HAART. Based on multivariate analysis, only the M184V mutation remained significantly associated with a viroimmunologic discordant response (odds ratio, 25.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.43 to 453.93). No difference in lamivudine exposure was found between discordant (95%) and failing (91%) patients. Twelve months after the genotypic analysis-guided change of therapy, 3 discordant (15%) and 6 failing patients (26%) achieved undetectable viral loads (<50 copies/ml), whereas in patients with HIV RNA loads of >500 copies/ml, discordant responses were observed in 5 out of 15 discordant patients and in 4 out of 16 failing patients. A relationship between the M184V mutation and a viroimmunologic discordant response to HAART was found. After the genotypic analysis-driven change of therapy, similar rates of virologic suppression were detected in the two groups.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study of the impact of HIV genotypic drug resistance testing on therapy efficacy.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001;63(5):447-73. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001. PMID: 11813503 Review.
-
Genotypic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 drug resistance in highly active antiretroviral therapy-treated children in Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005 Dec;24(12):1072-6. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000190413.88671.92. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. PMID: 16371868
-
Decrease of replicative capacity of HIV isolates after genotypic guided change of therapy.J Med Virol. 2004 Apr;72(4):511-6. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20030. J Med Virol. 2004. PMID: 14981751
-
Prevalence of mutations related to HIV-1 antiretroviral resistance in Brazilian patients failing HAART.J Clin Virol. 2002 Jul;25(1):39-46. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(01)00249-9. J Clin Virol. 2002. PMID: 12126720
-
On HIV diversity.AIDS. 2012 Jun 19;26(10):1255-60. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32835461b5. AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22706010 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment-mediated alterations in HIV fitness preserve CD4+ T cell counts but have minimal effects on viral load.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Nov 24;6(11):e1001012. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001012. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 21124866 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genotypes of gag sequences in HIV-1 infected children treated with antiretroviral therapy in Vietnam.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2020 Sep 17;7:2049936120958536. doi: 10.1177/2049936120958536. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32994994 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cells cross-present HIV antigens from live as well as apoptotic infected CD4+ T lymphocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 20;101(16):6092-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0304860101. Epub 2004 Apr 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15079077 Free PMC article.
-
Differential maintenance of the M184V substitution in the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by various nucleoside antiretroviral agents in tissue culture.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Nov;48(11):4189-94. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.11.4189-4194.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15504840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belec, L., C. Piketty, A. Si-Mohamed, C. Goujon, M. C. Hallouin, S. Cotigny, L. Weiss, and M. D. Kazatchkine. 2000. High levels of drug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus variants in patients exhibiting increasing CD4+ T cell counts despite virologic failure of protease inhibitor-containing antiretroviral combination therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 181:1808-1812. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter, C. C., D. A. Cooper, M. A. Fischl, J. M. Gatell, B. G. Gazzard, S. M. Hammer, M. S. Hirsch, D. M. Jacobsen, D. A. Katzenstein, J. S. Montaner, D. D. Richman, M. S. Saag, M. Schechter, R. T. Schooley, M. A. Thompson, S. Vella, P. G. Yeni, and P. A. Volberding. 2000. Antiretroviral therapy in adults: updated recommendations of the International AIDS Society-USA panel. JAMA 283:381-390. - PubMed
-
- Deeks, S. G., J. D. Barbour, R. M. Grant, and J. N. Martin. 2002. Duration and predictors of CD4 T-cell gains in patients who continue combination therapy despite detectable plasma viremia. AIDS 16:201-207. - PubMed
-
- Deeks, S. G., J. D. Barbour, J. N. Martin, M. S. Swanson, and R. M. Grant. 2000. Sustained CD4+ T cell response after virologic failure of protease inhibitor-based regimens in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 181:946-953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

