Evaluation of the clinical sensitivities of three viral load assays with plasma samples from a pediatric population predominantly infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype G and BG recombinant forms
- PMID: 12843094
- PMCID: PMC165345
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.7.3361-3367.2003
Evaluation of the clinical sensitivities of three viral load assays with plasma samples from a pediatric population predominantly infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype G and BG recombinant forms
Abstract
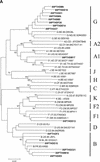
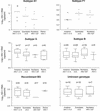
The viral load assays AMPLICOR HIV-1 Monitor Test 1.5, Nuclisens HIV-1 QT, and Quantiplex HIV RNA 3.0 (bDNA) were evaluated for their abilities to quantify human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA in 64 plasma samples from 21 children infected in Portugal. The children were infected with HIV-1 subtypes A1, B, F1, G, and BG recombinant virus. AMPLICOR v1.5 and Quantiplex v3.0 detected all samples, and there was a good correlation of results between the two kits. Thirty-eight specimens containing HIV-1 subtype B, G, or recombinant BG, could not be detected by Nuclisens HIV-1 QT. We also evaluated the new Retina HIV-1 assay on 21 samples that were HIV-1 positive; Retina HIV-1 failed to detect 5 of 11 subtype G specimens. AMPLICOR v1.5 and Quantiplex v3.0 assays may be used for HIV-1 RNA quantification in Portugal, whereas an improvement in sensitivity for subtype G and recombinant BG is required for Nuclisens HIV-1 QT and Retina HIV-1.
Figures

References
-
- Anastassopoulos, C. G., G. Touloumi, A. Katsoulidou, H. Hatzitheodorou, M. Pappa, D. Paraskevis, M. Lazanas, P. Gargalianos, and A. Hatzakis. 2001. Comparative evaluation of the Quantiplex HIV-1 RNA 2.0 and 3.0 (bDNA) assays and the Amplicor HIV-1 Monitor v1.5 test for the quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma. J. Virol. Methods 91:67-74. - PubMed
-
- Berndt, C., U. Muller, F. Bergmann, U. Schmitt, R. Kaiser, and C. Muller. 2000. Comparison between a nucleic acid sequence-based amplification and branched DNA test for quantifying HIV RNA load in blood plasma. J. Virol. Methods 89:177-181. - PubMed
-
- Burgisser, P., P. Vernazza, M. Flepp, J. Boni, Z. Tomasik, U. Hummel, G. Pantaleo, and J. Schupbach, et al. 2000. Performance of five different assays for the quantification of viral load in persons infected with various subtypes of HIV-1. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 23:138-144. - PubMed
-
- de Baar, M. P., A. M. Van Der Schoot, J. Goudsmit, F. Jacobs, R. Ehren, K. H. Van Der Horn, P. Oudshoorn, F. de Wolf, and A. de Ronde. 1999. Design and evaluation of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA assay using nucleic acid sequence-based amplification technology able to quantify both group M and O viruses by using the long terminal repeat as target. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37:1813-1818. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Baar, M. P., M. W. van Dooren, E. de Rooij, M. Bakker, B. van Gemen, J. Goudsmit, and A. de Ronde. 2001. Single rapid real-time monitored isothermal RNA amplification assay for quantification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates from groups M, N, and O. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:1378-1384. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

