Blockade of NMDA receptors in prelimbic cortex induces an enduring amnesia for odor-reward associative learning
- PMID: 12843246
- PMCID: PMC6741223
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05472.2003
Blockade of NMDA receptors in prelimbic cortex induces an enduring amnesia for odor-reward associative learning
Abstract
The competitive antagonist 2-amino-5-phosphonoeptanoic acid (APV) was injected intracerebroventricularly to determine the involvement of NMDA receptors in different stages of memory consolidation. Subsequent experiments used local injections to determine possible sites of drug action. Rats were trained in a rapidly learned olfactory task to find palatable food in a hole in a sponge impregnated with the target odor in the presence of two other sponges with nonrewarded odors. APV injections were made intracerebroventricularly 5 min or 2 hr after the end of the training, and a retention test was given 48 hr later. The results showed that blockade of NMDA receptors immediately after training induces a profound and enduring amnesia with no effect when the treatment is delayed at 2 hr after training. To address the question of the effective sites of action of the intracerebroventricular treatment, APV injections into the hippocampus and into the prelimblic region of the frontal cortex (PLC) were made. Blockade of NMDA receptors into the PLC but not into the hippocampus impaired memory formation of the odor-reward association. The amnesia is not transient, because the retention tests were made 48 hr after training. These results underlie the role of NMDA receptors in the early stage of consolidation of a simple odor-reward associative memory and confirm the role of the PLC in the consolidation of long-term memory.
Figures

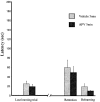
 p < 0.01). Significant differences were observed between the last trial of training and the retention test for the APV 5 min group (✻p < 0.01) and between the retention test and the relearning (★p < 0.01). Together, these data indicate that blockade of NMDA receptors immediately after training (1) induces amnesia with no effect when the treatment is 2 hr after training and (2) does not block the relearning.
p < 0.01). Significant differences were observed between the last trial of training and the retention test for the APV 5 min group (✻p < 0.01) and between the retention test and the relearning (★p < 0.01). Together, these data indicate that blockade of NMDA receptors immediately after training (1) induces amnesia with no effect when the treatment is 2 hr after training and (2) does not block the relearning.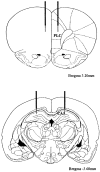
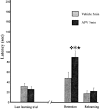
 p < 0.01). Significant differences were observed between the retention test and the last learning trial (✻p < 0.01) and between the retention test and the relearning (★p < 0.01) for the APV group. These data suggest that blockade of NMDA receptors into the prelimbic cortex after the training induces amnesia but does not block the relearning.
p < 0.01). Significant differences were observed between the retention test and the last learning trial (✻p < 0.01) and between the retention test and the relearning (★p < 0.01) for the APV group. These data suggest that blockade of NMDA receptors into the prelimbic cortex after the training induces amnesia but does not block the relearning.Similar articles
-
Reconsolidation after remembering an odor-reward association requires NMDA receptors.Learn Mem. 2005 Jan-Feb;12(1):18-22. doi: 10.1101/lm.80905. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Learn Mem. 2005. PMID: 15647596 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of muscarinic receptor blockade in prelimbic cortex on acquisition and memory formation of an odor-reward task.Learn Mem. 2007 Sep 6;14(9):616-24. doi: 10.1101/lm.597507. Print 2007 Sep. Learn Mem. 2007. PMID: 17848501 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor-dependent processes in the medial prefrontal cortex are important for acquisition and the early stage of consolidation during trace, but not delay eyeblink conditioning.Learn Mem. 2005 Nov-Dec;12(6):606-14. doi: 10.1101/lm.5905. Learn Mem. 2005. PMID: 16322362 Free PMC article.
-
Associative learning: Hebbian flies.Curr Biol. 2005 Jun 7;15(11):R416-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.028. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15936261 Review.
-
The role of protein synthesis in memory consolidation: progress amid decades of debate.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2008 Mar;89(3):293-311. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2007.09.010. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2008. PMID: 18053752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial encoding in dorsomedial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus is related during deliberation.Hippocampus. 2020 Nov;30(11):1194-1208. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23250. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Hippocampus. 2020. PMID: 32809246 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Information Storage Engages Subcortical and Cortical Brain Regions That Support Valence Determination.Cereb Cortex. 2022 Feb 8;32(4):689-708. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhab226. Cereb Cortex. 2022. PMID: 34379749 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term memory, synaptic plasticity and dopamine in rodent medial prefrontal cortex: Role in executive functions.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Jan 11;16:1068271. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1068271. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36710953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconsolidation after remembering an odor-reward association requires NMDA receptors.Learn Mem. 2005 Jan-Feb;12(1):18-22. doi: 10.1101/lm.80905. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Learn Mem. 2005. PMID: 15647596 Free PMC article.
-
Offline orbitofrontal cortex reactivation depends on recency of place-reward changes and coheres with hippocampal replay.iScience. 2024 Feb 10;27(3):109205. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109205. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38482496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Datiche F, Cattarelli M ( 1996) Reciprocal and topgraphic connections between the piriform and prefrontal cortices in the rat: a tracing study using the B subunit of the cholera toxin. Brain Res Bull 41: 391–398. - PubMed
-
- Dusek JA, Eichenbaum H ( 1998) The hippocampus and transverse patterning guided by olfactory cues. Behav Neurosci 112: 762–771. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira MB, Da Silva RC, Medina JH, Izquierdo I ( 1992) Late posttraining memory processing by entorhinal cortex: involvement of NMDA and GABAergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41: 767–771. - PubMed
-
- Izquierdo I, Da Cunha C, Rosat R, Jerusalinsky D, Ferreira MB, Medina JH ( 1992) Neurotransmitter receptors involved in post-training memory processing by the amygdala, medial septum, and hippocampus of the rat. Behav Neural Biol 58: 16–26. - PubMed
-
- Jerusalinsky D, Ferreira MB, Walz R, Da Silva RC, Bianchin M, Ruschel AC, Zanatta MS, Medina JH, Izquierdo I ( 1992) Amnesia by post-training infusion of glutamate receptor antagonists into the amygdala, hippocampus, and entorhinal cortex. Behav Neural Biol 58: 76–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
